Peptide hormones in plants
- PMID: 39849641
- PMCID: PMC11756074
- DOI: 10.1186/s43897-024-00134-y
Peptide hormones in plants
Abstract
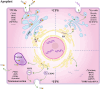
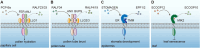
Peptide hormones are defined as small secreted polypeptide-based intercellular communication signal molecules. Such peptide hormones are encoded by nuclear genes, and often go through proteolytic processing of preproproteins and post-translational modifications. Most peptide hormones are secreted out of the cell to interact with membrane-associated receptors in neighboring cells, and subsequently activate signal transductions, leading to changes in gene expression and cellular responses. Since the discovery of the first plant peptide hormone, systemin, in tomato in 1991, putative peptide hormones have continuously been identified in different plant species, showing their importance in both short- and long-range signal transductions. The roles of peptide hormones are implicated in, but not limited to, processes such as self-incompatibility, pollination, fertilization, embryogenesis, endosperm development, stem cell regulation, plant architecture, tissue differentiation, organogenesis, dehiscence, senescence, plant-pathogen and plant-insect interactions, and stress responses. This article, collectively written by researchers in this field, aims to provide a general overview for the discoveries, functions, chemical natures, transcriptional regulations, and post-translational modifications of peptide hormones in plants. We also updated recent discoveries in receptor kinases underlying the peptide hormone sensing and down-stream signal pathways. Future prospective and challenges will also be discussed at the end of the article.
Keywords: Peptide hormones; Post-translational modifications; Proteolytic processing; Receptor-like kinase; Secretions; Signal transductions.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: All authors approve the manuscript and consent to publication of the work. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests exist. Yongfeng Guo and Chuanyou Li are members of the Editorial Board for Molecular Horticulture and were not involved in the journal’s review of, or decisions related to, this manuscript.
Figures


References
-
- Abdullah FS, Mehmood F, et al. The GASA gene family in Cacao (Theobroma cacao, Malvaceae): genome wide identification and expression analysis. Agronomy. 2021;11:1425. 10.3390/agronomy11071425.
-
- Aghdam MS, Alikhani-Koupaei M. Exogenous phytosulfokine α (PSKα) applying delays senescence and relief decay in strawberry fruits during cold storage by sufficient intracellular ATP and NADPH availability. Food Chem. 2021;336:127685. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127685. - PubMed
-
- Aghdam MS, Flores FB. Employing phytosulfokine α (PSKα) for delaying broccoli florets yellowing during cold storage. Food Chem. 2021;355:129626. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129626. - PubMed
-
- Aghdam MS, Sayyari M, Luo Z. Exogenous application of phytosulfokine α (PSKα) delays yellowing and preserves nutritional quality of broccoli florets during cold storage. Food Chem. 2020;333:127481. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127481. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 32270332/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32370850/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32170332/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32230009/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32230077/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- U22A20474/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32172073/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- ASTIP-TRI02/Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program of China, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences
- 2020JC-29/Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi
- 2023-JC-ZD-09/Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi
- GK202402003/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- 21ZDKA0016/Foundation of Science and Technology of Gansu Province
- 22ZD6NA049/Foundation of Science and Technology of Gansu Province
- 2021YFF1000201/National Key R&D Program of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
