Effect of Sequential, Colocalized Radiofrequency and Pulsed Field Ablation on Cardiac Lesion Size and Histology
- PMID: 39851044
- PMCID: PMC11837966
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCEP.124.013143
Effect of Sequential, Colocalized Radiofrequency and Pulsed Field Ablation on Cardiac Lesion Size and Histology
Abstract
Background: Sequential application of radiofrequency with pulsed field (PF) ablation may increase lesion depth while preserving the advantages of PF. The study's aim was to determine lesion dimensions of sequential, colocalized radiofrequency and PF ablation.
Methods: A preclinical study using swine (n=4) performed lesions in the right/left ventricles. Ablations were performed with a force-sensing 3.5-mm irrigated-tip ablation catheter using a generator delivering both radiofrequency and PF. PF was delivered using unipolar, biphasic pulses at a standard dose (PF index, 300) with 4-mL/min irrigation. Radiofrequency was delivered at 50 W for 10 s (15 mL/min). Lesions were created by applying colocalized radiofrequency followed by sequential application of PF on the same location, PF followed by sequential application of radiofrequency on the same location, PF alone, or radiofrequency alone. Tissue was collected after 2 hours for lesion assessment. Results are mean±SD.
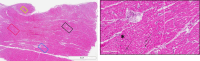
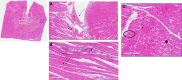
Results: Forty-five lesions were analyzed. The lesion depth of radiofrequency alone was 4.9±0.8 mm. The mean lesion depth and width for PF alone were 3.5±0.6 and 5.1±1.8 mm. Lesion depths for combined applications were significantly greater versus PF alone (6.2±1.8 mm radiofrequency followed by sequential application of PF on the same location; 5.7±1.3 mm PF followed by sequential application of radiofrequency on the same location; P<0.0001 for both). Lesion widths were also significantly greater with combined therapy versus PF alone (8.6±1.8 mm radiofrequency followed by sequential application of PF on the same location; 8.9±2.1 mm PF followed by sequential application of radiofrequency on the same location; P<0.0001 for both). Histology for both combined lesions showed central thermal necrosis surrounded by a hemorrhagic and transitional PF zone.
Conclusions: Combined, colocalized radiofrequency and PF, irrespective of order, show significantly increased lesion size compared with the same dose of PF or radiofrequency alone.
Keywords: ablation; catheters; heart atria; heart ventricles; irreversible electroporation therapy; models, animal; technology.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Verma reports consulting/advisory to Biosense Webster, Inc, Medtronic, Abbott, MedLumics, and Adagio Medical. J. Maffre and Drs Sharma and Farshchi-Heydari are employees of Biosense Webster, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Verma A, Asivatham SJ, Deneke T, Castellvi Q, Neal RE, Castellvi Q, Neal RE, 2nd. Primer on pulsed electrical field ablation: understanding the benefits and limitations. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2021;14:e010086. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.121.010086 - PubMed
-
- Verma A, Haines DE, Boersma LV, Sood N, Natale A, Marchlinski FE, Calkins H, Sanders P, Packer DL, Kuck KH, et al. ; PULSED AF Investigators. Pulsed field ablation for the treatment of atrial fibrillation: PULSED AF pivotal trial. Circulation. 2023;147:1422–1432. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.123.063988 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duytschaever M, De Potter T, Grimaldi M, Anic A, Vijgen J, Neuzil P, Van Herendael H, Verma A, Skanes A, Scherr D, et al. ; inspIRE Trial Investigators. Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation ablation using a novel variable-loop biphasic pulsed field ablation catheter integrated with a 3-dimensional mapping system: 1-year outcomes of the multicenter inspIRE study. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2023;16:e011780. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.122.011780 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reddy VY, Gerstenfeld EP, Natale A, Whang W, Cuoco FA, Patel C, Mountantonakis SE, Gibson DN, Harding JD, Ellis CR, et al. ; ADVENT Investigators. Pulsed field or conventional thermal ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2023;389:1660–1671. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2307291 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

