Hyaluronic Acid-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 39851489
- PMCID: PMC11764402
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14020061
Hyaluronic Acid-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
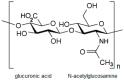
In recent years, hyaluronic acid (HA) has attracted increasing attention as a promising biomaterial for the development of drug delivery systems. Due to its unique properties, such as high biocompatibility, low toxicity, and modifiability, HA is becoming a basis for the creation of targeted drug delivery systems, especially in the field of oncology. Receptors for HA overexpressed in subpopulations of cancer cells, and one of them, CD44, is recognized as a molecular marker for cancer stem cells. This review examines the role of HA and its receptors in health and tumors and analyzes existing HA-based delivery systems and their use in various types of cancer. The development of new HA-based drug delivery systems will bring new opportunities and challenges to anti-cancer therapy.
Keywords: cancer therapy; drug delivery system; extracellular matrix; hyaluronic acid; nanoparticle; supramolecular system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wang J., Wang D., Cen M., Jing D., Bei J., Huang Y., Zhang J., Lu B., Wang Y., Yao Y. GOx-assisted synthesis of pillar[5]arene based supramolecular polymeric nanoparticles for targeted/synergistic chemo-chemodynamic cancer therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022;20:33. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-01237-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

