Gut Microbiome Modulation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Preventive Role in NAFLD/NASH Progression and Potential Applications in Immunotherapy-Based Strategies
- PMID: 39851512
- PMCID: PMC11764391
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14020084
Gut Microbiome Modulation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Preventive Role in NAFLD/NASH Progression and Potential Applications in Immunotherapy-Based Strategies
Abstract
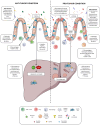
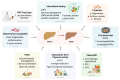
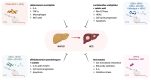
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a heterogeneous tumor associated with several risk factors, with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) emerging as an important cause of liver tumorigenesis. Due to the obesity epidemics, the occurrence of NAFLD has significantly increased with nearly 30% prevalence worldwide. HCC often arises in the background of chronic liver disease (CLD), such as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and cirrhosis. Gut microbiome (GM) alterations have been linked to NAFLD progression and HCC development, with several investigations reporting a crucial role for the gut-liver axis and microbial metabolites in promoting CLD. Moreover, the GM affects liver homeostasis, energy status, and the immune microenvironment, influencing the response to immunotherapy with interesting therapeutic implications. In this review, we summarize the main changes in the GM and derived metabolites (e.g., short-chain fatty acids and bile acids) occurring in HCC patients and influencing NAFLD progression, emphasizing their potential as early diagnostic biomarkers and prognostic tools. We discuss the weight loss effects of diet-based interventions and healthy lifestyles for the treatment of NAFLD patients, highlighting their impact on the restoration of the intestinal barrier and GM structure. We also describe encouraging preclinical findings on the modulation of GM to improve liver functions in CLD, boost the antitumor immune response (e.g., probiotic supplementations or anti-hypercholesterolemic drug treatment), and ultimately delay NAFLD progression to HCC. The development of safe and effective strategies that target the gut-liver axis holds promise for liver cancer prevention and treatment, especially if personalized options will be considered.
Keywords: HCC; NAFLD; immunotherapy; microbiome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Riazi K., Azhari H., Charette J.H., Underwood F.E., King J.A., Afshar E.E., Swain M.G., Congly S.E., Kaplan G.G., Shaheen A.-A. The Prevalence and Incidence of NAFLD Worldwide: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022;7:851–861. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00165-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Estes C., Anstee Q.M., Arias-Loste M.T., Bantel H., Bellentani S., Caballeria J., Colombo M., Craxi A., Crespo J., Day C.P., et al. Modeling NAFLD Disease Burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the Period 2016–2030. J. Hepatol. 2018;69:896–904. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.05.036. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Reig M., Forner A., Rimola J., Ferrer-Fàbrega J., Burrel M., Garcia-Criado Á., Kelley R.K., Galle P.R., Mazzaferro V., Salem R., et al. BCLC Strategy for Prognosis Prediction and Treatment Recommendation: The 2022 Update. J. Hepatol. 2022;76:681–693. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.11.018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

