Immune Gene Expression Profiling in Individuals with Turner Syndrome, Graves' Disease, and a Healthy Female by Single-Cell RNA Sequencing: A Comparative Study
- PMID: 39851522
- PMCID: PMC11764232
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14020093
Immune Gene Expression Profiling in Individuals with Turner Syndrome, Graves' Disease, and a Healthy Female by Single-Cell RNA Sequencing: A Comparative Study
Abstract
Turner syndrome (TS) can be determined by karyotype analysis, marked by the loss of one X chromosome in females. However, the genes involved in autoimmunity in TS patients remain unclear. In this study, we aimed to analyze differences in immune gene expression between a patient with TS, a healthy female, and a female patient with Graves' disease using single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) analysis of antigen-specific CD4(+) T cells. We identified 43 differentially expressed genes in the TS patient compared with the healthy female and the female patient with Graves' disease. Many of these genes have previously been suggested to play a role in immune system regulation. This study provides valuable insights into the differences in immune-related gene expression between TS patients, healthy individuals, and those with autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: Turner syndrome; X chromosome inactivation; autoimmunity; gene expression; single-cell RNA analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
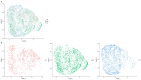

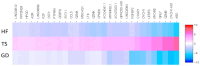

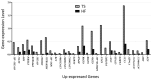


References
-
- Zenaty D., Laurent M., Carel J.C., Léger J. Turner Syndrome: What’s new in medical care? Arch. Pediatr. 2011;18:1343–1347. - PubMed
-
- Berglund A., Viuff M.H., Skakkebaek A., Chang S., Stochholm K., Gravholt C.H. Changes in the cohort composition of turner syndrome and severe non-diagnosis of Klinefelter, 47,XXX and 47,XYY syndrome: A nationwide cohort study. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019;14:16. doi: 10.1186/s13023-018-0976-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

