Impacts of Hyaluronan on Extracellular Vesicle Production and Signaling
- PMID: 39851567
- PMCID: PMC11763598
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14020139
Impacts of Hyaluronan on Extracellular Vesicle Production and Signaling
Abstract
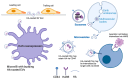
Hyaluronan (HA) is a critical component of cell and tissue matrices and an important signaling molecule. The enzymes that synthesize and process HA, as well as the HA receptors through which the signaling properties of HA are transmitted, have been identified in extracellular vesicles and implicated in context-specific processes associated with health and disease. The goal of this review is to present a comprehensive summary of the research on HA and its related receptors and enzymes in extracellular vesicle biogenesis and the cellular responses to vesicles bearing these extracellular matrix modulators. When present in extracellular vesicles, HA is assumed to be on the outside of the vesicle and is sometimes found associated with CD44 or the HAS enzyme itself. Hyaluronidases may be inside the vesicles or present on the vesicle surface via a transmembrane domain or GPI linkage. The implication of presenting these signals in extracellular vesicles is that there is a greater range of systemic distribution and more complex delivery media than previously thought for secreted HA or hyaluronidase alone. Understanding the context for these HA signals offers new diagnostic and therapeutic insight.
Keywords: CD44; cancer; exosomes; extracellular vesicles; hyaluronan; hyaluronidase; microvesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

