Microlipophagy from Simple to Complex Eukaryotes
- PMID: 39851569
- PMCID: PMC11764314
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14020141
Microlipophagy from Simple to Complex Eukaryotes
Abstract
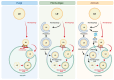
Lipophagy is a selective degradation of lipid droplets in lysosomes or vacuoles. Apart from its role in generating energy and free fatty acids for membrane repair, growth, and the formation of new membranes, lipophagy emerges as a key player in other cellular processes and disease pathogenesis. While fungal, plant, and algal cells use microlipophagy, the most prominent form of lipophagy in animal cells is macrolipophagy. However, recent studies showed that animal cells can also use microlipophagy to metabolize their lipid droplets. Therefore, to no surprise, microlipophagy is conserved from simple unicellular to the most complex multicellular eukaryotes, and many eukaryotic cells can operate both forms of lipophagy. Macrolipophagy is the most studied and better understood at the molecular level, while our understanding of microlipophagy is very sparse. This review will discuss microlipophagy from the perspective of its conservation in eukaryotes and its importance in diseases. To better appreciate the conserved nature of microlipophagy, different organisms and types of cells in which microlipophagy has been reported are also shown in a tabular form. We also point toward the gaps in our understanding of microlipophagy, including the signaling behind microlipophagy, especially in the cells of complex multicellular organisms.
Keywords: autophagy; chaperon-mediated autophagy; lipid droplets; lipophagy; macroautophagy; macrolipophagy; microautophagy; microlipophagy; selective autophagy; vacuolar microdomains.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lipid Droplets and Their Autophagic Turnover via the Raft-Like Vacuolar Microdomains.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 29;22(15):8144. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158144. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ménage à trois of autophagy, lipid droplets and liver disease.Autophagy. 2022 Jan;18(1):50-72. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1895658. Epub 2021 Apr 2. Autophagy. 2022. PMID: 33794741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Greatwall kinase Rim15 promotes microautophagy and microlipophagy under the control of TORC1.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025 Mar 8;752:151468. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2025.151468. Epub 2025 Feb 9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 39952117
-
The regulation, function, and role of lipophagy, a form of selective autophagy, in metabolic disorders.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Feb 8;13(2):132. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04593-3. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35136038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid droplet autophagy during energy mobilization, lipid homeostasis and protein quality control.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2018 Mar 1;23(8):1552-1563. doi: 10.2741/4660. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2018. PMID: 29293450 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Klionsky D.J., Abdel-Aziz A.K., Abdelfatah S., Abdellatif M., Abdoli A., Abel S., Abeliovich H., Abildgaard M.H., Abudu Y.P., Acevedo-Arozena A., et al. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (4th edition)(1) Autophagy. 2021;17:1–382. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1797280. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

