Current Status and Future Directions of Artificial Intelligence in Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Literature Measurement Analysis
- PMID: 39851830
- PMCID: PMC11760884
- DOI: 10.3390/bs15010027
Current Status and Future Directions of Artificial Intelligence in Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Literature Measurement Analysis
Abstract
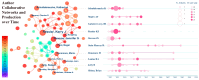
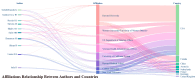
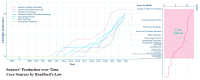
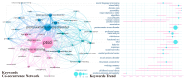
This study aims to explore the current state of research and the applicability of artificial intelligence (AI) at various stages of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), including prevention, diagnosis, treatment, patient self-management, and drug development. We conducted a bibliometric analysis using software tools such as Bibliometrix (version 4.1), VOSviewer (version 1.6.19), and CiteSpace (version 6.3.R1) on the relevant literature from the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC). The analysis reveals a significant increase in publications since 2017. Kerry J. Ressler has emerged as the most influential author in the field to date. The United States leads in the number of publications, producing seven times more papers than Canada, the second-ranked country, and demonstrating substantial influence. Harvard University and the Veterans Health Administration are also key institutions in this field. The Journal of Affective Disorders has the highest number of publications and impact in this area. In recent years, keywords related to functional connectivity, risk factors, and algorithm development have gained prominence. The field holds immense research potential, with AI poised to revolutionize PTSD management through early symptom detection, personalized treatment plans, and continuous patient monitoring. However, there are numerous challenges, and fully realizing AI's potential will require overcoming hurdles in algorithm design, data integration, and societal ethics. To promote more extensive and in-depth future research, it is crucial to prioritize the development of standardized protocols for AI implementation, foster interdisciplinary collaboration-especially between AI and neuroscience-and address public concerns about AI's role in healthcare to enhance its acceptance and effectiveness.
Keywords: Bibliometrix; CiteSpace; VOSviewer; algorithm; artificial intelligence; bibliometric analysis; digital psychiatry; post-traumatic stress disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest, and the funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures









References
-
- Abd-Alrazaq A., Alhuwail D., Schneider J., Toro C. T., Ahmed A., Alzubaidi M., Alajlani M., Househ M. The performance of artificial intelligence-driven technologies in diagnosing mental disorders: An umbrella review. NPJ Digital Medicine. 2022;5(1):87. doi: 10.1038/s41746-022-00631-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aria M., Cuccurullo C. bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. Journal of Informetrics. 2017;11(4):959–975. doi: 10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007. - DOI
-
- Atari-Khan R., Covington A. H., Gerstein L. H., Herz H. A., Varner B. R., Brasfield C., Shurigar B., Hinnenkamp S. F., Devia M., Barrera S., Deogracias-Schleich A. Concepts of resilience among trauma-exposed Syrian refugees. The Counseling Psychologist. 2021;49(2):233–268. doi: 10.1177/0011000020970522. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

