Comparison of CT-Guided Microwave Ablation of Liver Malignancies with and Without Intra-Arterial Catheter Placement for Contrast Administration
- PMID: 39851944
- PMCID: PMC11764381
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol32010028
Comparison of CT-Guided Microwave Ablation of Liver Malignancies with and Without Intra-Arterial Catheter Placement for Contrast Administration
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to compare microwave ablation (MWA) with and without prior placement of an intra-arterial catheter for the purpose of application of contrast medium (CM).
Methods: 148 patients (45 female, 65.1 ± 14.9 years) with liver tumors who underwent CT-guided MWA were included. Of these, 25 patients had an IA catheter placed in the hepatic artery.
Results: 37 patients underwent planning imaging for MWA without CM. A total of 86 patients received a standard dose of 80 mL intravenous (IV) CM for the planning scans. The patients with an IA catheter (n = 25) received an IA application of 10 mL CM. A total of 29 patients received contrast-enhanced scans in the PV phase for control of needle positioning after IV application of a standard dose of 80 mL CM. In patients with an IA catheter, control of the needle position was performed by single-slice scans. IA CM application during the ablation enabled monitoring of the ablation zone. Over the entire intervention, patients with IA catheters received less CM as compared to patients without an IA catheter (39.1 ± 10.4 mL vs. 141 ± 39.69 mL; p < 0.001).
Conclusions: IA catheter placement was associated with a significant decrease of the amount of CM during MWA and enabled monitoring of the ablation zone.
Keywords: hepatic malignancies; intra-arterial catheter placement; microwave ablation of the liver.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
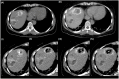
References
-
- Wade R., South E., Anwer S., Sharif-Hurst S., Harden M., Fulbright H., Hodgson R., Dias S., Simmonds M., Rowe I., et al. Ablative and non-surgical therapies for early and very early hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Health Technol. Assess. 2023;27:1–172. doi: 10.3310/GK5221. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shi Q., Zhang Z., Zhang W., Ma J., Yang M., Luo J., Liu L., Yan Z. Microwave ablation combined with transarterial chemoembolization containing doxorubicin hydrochloride liposome for treating primary and metastatic liver cancers. J. Interv. Med. 2023;6:121–125. doi: 10.1016/j.jimed.2023.07.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biondetti P., Ierardi A.M., Casiraghi E., Caruso A., Grillo P., Carriero S., Lanza C., Angileri S.A., Sangiovanni A., Iavarone M., et al. Clinical Impact of a Protocol Involving Cone-Beam CT (CBCT), Fusion Imaging and Ablation Volume Prediction in Percutaneous Image-Guided Microwave Ablation in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Unsuitable for Standard Ultrasound (US) Guidance. J. Clin. Med. 2023;12:7598. doi: 10.3390/jcm12247598. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

