Rebiopsy Enhances Survival with Afatinib vs. Osimertinib in EGFR Exon 19 Deletion Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Multicenter Study in Taiwan
- PMID: 39851952
- PMCID: PMC11763488
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol32010036
Rebiopsy Enhances Survival with Afatinib vs. Osimertinib in EGFR Exon 19 Deletion Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Multicenter Study in Taiwan
Abstract
Background: Afatinib and Osimertinib are first-line treatments for EGFR-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), but their comparative efficacies and the patient groups that benefit the most remain unclear. This multicenter retrospective study evaluated the efficacy of first-line Afatinib and Osimertinib in NSCLC patients with EGFR 19del and no brain metastases at diagnosis.
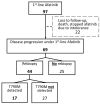
Methods: The primary endpoints were time on treatment (ToT) and overall survival (OS). Survival analyses were performed for three groups: Afatinib followed by Osimertinib, Afatinib followed by other therapies, and Osimertinib (alone or followed by other therapies). Rebiopsy practices, including T790M mutation detection, were also analyzed in patients with disease progression on Afatinib.
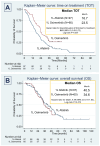
Results: Among 97 Afatinib-treated and 60 Osimertinib-treated patients, Osimertinib showed a significantly longer ToT (23.3 vs. 16.5 months; p = 0.007). Median OS was numerically higher for Afatinib with sequential Osimertinib (40.5 vs. 34.6 months for Osimertinib; p = 0.473). Osimertinib demonstrated advantages, with fewer brain metastases upon progression and fewer adverse effects. In the Afatinib group, 64% of patients with disease progression underwent rebiopsy, with 39% testing positive for T790M mutation and subsequently receiving Osimertinib. Rebiopsy was most frequently performed on the lung parenchyma using non-surgical methods.
Conclusions: In this real-world study, Osimertinib achieved a significantly longer ToT compared to Afatinib in NSCLC patients with EGFR 19del and no brain metastases. The sequential use of Afatinib followed by Osimertinib showed a trend toward improved OS, highlighting the importance of rebiopsy for identifying T790M mutations to guide subsequent therapy.
Keywords: Afatinib; EGFR mutation; Osimertinib; lung cancer; rebiopsy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests that could have influenced the work reported in this paper. The Abstract of this paper was presented at the 2022 Annual Congress of Taiwan Society of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine as a poster presentation with interim findings. The poster’s Abstract was published in “Poster Abstracts” in
Figures


References
-
- Barlesi F., Mazieres J., Merlio J.P., Debieuvre D., Mosser J., Lena H., Ouafik L., Besse B., Rouquette I., Westeel V., et al. Routine molecular profiling of patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Results of a 1-year nationwide programme of the French Cooperative Thorac-ic Intergroup (IFCT) Lancet. 2016;387:1415–1426. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00004-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kris M.G., Johnson B.E., Berry L.D., Kwiatkowski D.J., Iafrate A.J., Wistuba I.I., Varella-Garcia M., Franklin W.A., Aronson S.L., Su P.F., et al. Using multiplexed assays of oncogenic drivers in lung cancers to select targeted drugs. JAMA. 2014;311:1998–2006. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.3741. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shi Y., Au J.S., Thongprasert S., Srinivasan S., Tsai C.M., Khoa M.T., Heeroma K., Itoh Y., Cornelio G., Yang P.C. A prospective, molecular epidemi-ology study of EGFR mutations in Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology (PIONEER) J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014;9:154–162. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000033. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (Version 4.2022). 2 September 2022. [(accessed on 15 September 2022)]. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf.
-
- Reungwetwattana T., Nakagawa K., Cho B.C., Cobo M., Cho E.K., Bertolini A., Bohnet S., Zhou C., Lee K.H., Nogami N., et al. CNS Response to Osimertinib Versus Standard Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Patients with Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018;36:3290–3297. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.78.3118. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

