Natural Bletilla striata Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels for Accelerating Hemostasis
- PMID: 39852020
- PMCID: PMC11764679
- DOI: 10.3390/gels11010048
Natural Bletilla striata Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels for Accelerating Hemostasis
Abstract
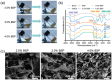
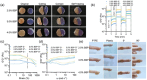
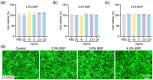
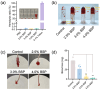
Most of the existing hydrogel dressings have inadequacies in mechanical performance, biological activities, compatibility, or versatility, which results in the development of rapid, green, and cost-effective approaches for hydrogels in biochemical and biomedical applications becoming a top-priority task. Herein, inspired by the inherent bioactivity, water retention properties, and biocompatibility of natural polysaccharide hydrogels, we have prepared self-healing gels. Using Bletilla striata polysaccharide (BSP), carboxymethyl chitosan (CMCS), and borax via borate ester linkages, we created hemostatic and self-healing Chinese herbal medicine hydrogels in varying concentrations (2.5%, 3.0%, and 4.0%). A rotational rheometer was used to describe the hydrogels' shape and rheological characteristics. At all concentrations, it was found that the hydrogels' elastic modulus (G') consistently and significantly outperformed their viscous modulus (G″), suggesting a robust internal structure. All of the hydrogels had cell viability levels as high as 100% and hemolysis rates below 1%, indicating the hydrogels' outstanding biocompatibility. Furthermore, the hydrogels demonstrated superior hemostatic qualities in an in vivo mouse tail amputation model, as well as in in vitro coagulation tests. The results show that the hydrogel possesses excellent self-healing properties, as well as a good biocompatibility and hemostatic performance, thus paving the way for the development of a potential hemostatic green hydrogel.
Keywords: Bletilla striata polysaccharide; borate ester bonds; hemostasis; hydrogels; natural.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest. The funders did not play any role in the design of the study; the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; the writing of the manuscript; or the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Self-healing, antioxidant, and antibacterial Bletilla striata polysaccharide-tannic acid dual dynamic crosslinked hydrogels for tissue adhesion and rapid hemostasis.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Jun;270(Pt 2):132182. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.132182. Epub 2024 May 7. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38723806
-
Preparation and evaluation of Bletilla striata polysaccharide/carboxymethyl chitosan/Carbomer 940 hydrogel for wound healing.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Jul 1;132:729-737. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.157. Epub 2019 Mar 30. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 30940589
-
Biocompatible and biodegradable Bletilla striata polysaccharides hydrogels crosslinked by BDDE for wound healing through the regulating of macrophage polarization.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Jan;254(Pt 3):128015. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.128015. Epub 2023 Nov 10. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 37951426
-
Dual properties of pharmacological activities and preparation excipient: Bletilla striata polysaccharides.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Jan;254(Pt 1):127643. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127643. Epub 2023 Oct 26. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 37898246 Review.
-
Bletilla striata: Medicinal uses, phytochemistry and pharmacological activities.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Jan 4;195:20-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.11.026. Epub 2016 Nov 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27865796 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

