Machine Learning-Based Quantification of Lateral Flow Assay Using Smartphone-Captured Images
- PMID: 39852070
- PMCID: PMC11763061
- DOI: 10.3390/bios15010019
Machine Learning-Based Quantification of Lateral Flow Assay Using Smartphone-Captured Images
Abstract
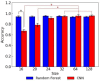
Lateral flow assay has been extensively used for at-home testing and point-of-care diagnostics in rural areas. Despite its advantages as convenient and low-cost testing, it suffers from poor quantification capacity where only yes/no or positive/negative diagnostics are achieved. In this study, machine learning and deep learning models were developed to quantify the analyte load from smartphone-captured images of the lateral flow assay test. The comparative analysis identified that random forest and convolutional neural network (CNN) models performed well in classifying the lateral flow assay results compared to other well-established machine learning models. When trained on small-size images, random forest models excelled CNN models in image classification. Contrarily, CNN models outperformed random forest models in classifying noisy images.
Keywords: CNN; deep learning; lateral flow assay; machine learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Yousufuddin M., Mahmood M., Barkoudah E., Badr F., Khandelwal K., Manyara W., Sharma U., Abdalrhim A.D., Issa M., Bhagra S., et al. Rural-urban Differences in Long-term Mortality and Readmission Following COVID-19 Hospitalization, 2020 to 2023. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2024;11:ofae197. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofae197. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

