Development and Validation of LAMP Assays for Distinguishing MPXV Clades with Fluorescent and Colorimetric Readouts
- PMID: 39852076
- PMCID: PMC11764415
- DOI: 10.3390/bios15010023
Development and Validation of LAMP Assays for Distinguishing MPXV Clades with Fluorescent and Colorimetric Readouts
Abstract
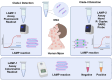
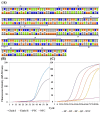
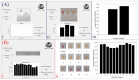
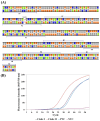
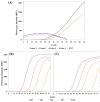
Human monkeypox (Mpox) is a zoonotic disease caused by the Monkeypox virus (MPXV). As of 14 August 2024, the World Health Organization (WHO) has declared it a global health emergency. For Mpox, this was the second public health emergency of global significance in the past two years. MPXV belongs to the Poxviridae family and is phylogenetically and epidemically divided into two clades: the Congo Basin (Clade-I) and the West African (Clade-II) clades. Clade-I has been associated with more severe disease progression and higher mortality compared to Clade-II, and thus the differentiation between clades can play an important role in predicting disease prognosis. The LAMP technique has the advantages of not requiring thermal cycling and achieving higher amplification in a shorter time compared to qPCR. Different types of LAMP assays were developed in this study to benefit from these advantages. We report the development of LAMP-1 and LAMP-2 assays using the LAMP method to detect MPXV Clade-I and Clade-II, respectively. The LAMP-1 assay includes both fluorescence and visible colorimetric readout tests developed with sensitivities of 103 and 107 copies, respectively. For the LAMP-2 assay, a probe-based test utilizing the Novel R-Duplex DARQ probe was developed, offering fluorescence detection at a sensitivity of 103 copies. As a result, we successfully developed three highly specific molecular diagnostic tests that distinctly differentiate between MPXV clades, delivering essential tools for the precise diagnosis and effective control of Mpox.
Keywords: loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology; monkeypox virus clade detection; novel reverse-duplex detection of amplification by release of quenching probe.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aslan M., Seymour E., Brickner H., Clark A.E., Celebi I., Townsend M.B., Satheshkumar P.S., Riley M., Carlin A.F., Ünlü M.S., et al. A Label-free Optical Biosensor-Based Point-of-Care Test for the Rapid Detection of Monkeypox Virus. medRxiv. 2024 doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2024.116932. medRxiv:2024.07.03.24309903. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Magnus P.v., Andersen E.K., Petersen K.B., Birch-Andersen A. A pox-like disease in cynomolgus monkeys. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. 1959;46:156–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1959.tb00328.x. - DOI
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

