SERS Detection of Hydrophobic Molecules: Thio-β-Cyclodextrin-Driven Rapid Self-Assembly of Uniform Silver Nanoparticle Monolayers and Analyte Trapping
- PMID: 39852103
- PMCID: PMC11763657
- DOI: 10.3390/bios15010052
SERS Detection of Hydrophobic Molecules: Thio-β-Cyclodextrin-Driven Rapid Self-Assembly of Uniform Silver Nanoparticle Monolayers and Analyte Trapping
Abstract
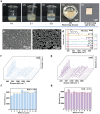
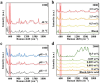
High-sensitivity and repeatable detection of hydrophobic molecules through the surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) technique is a tough challenge because of their weak adsorption and non-uniform distribution on SERS substrates. In this research, we present a simple self-assembly protocol for monolayer SERS mediated by 6-deoxy-6-thio-β-cyclodextrin (β-CD-SH). This protocol allows for the rapid assembly of a compact silver nanoparticle (Ag NP) monolayer at the oil/water interface within 40 s, while entrapping analyte molecules within hotspots. The proposed method shows general applicability for detecting hydrophobic molecules, exemplified as Nile blue, Nile red, fluconazole, carbendazim, benz[a]anthracene, and bisphenol A. The detection limits range from 10-6to 10-9 M, and the relative standard deviations (RSDs) of signal intensity are less than 10%. Moreover, this method was used to investigate the release behaviors of a hydrophobic pollutant (Nile blue) adsorbed on the nanoplastic surface in the water environment. The results suggest that elevated temperatures, increased salinities, and the coexistence of fulvic acid promote the release of Nile blue. This simple and fast protocol overcomes the difficulties related to hotspot accessibility and detection repeatability for hydrophobic analytes, holding out extensive application prospects in environmental monitoring and chemical analysis.
Keywords: SERS; hydrophobic analyte; self-assembly film; silver nanoparticle; β-CD-SH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Simultaneous and rapid determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by facile and green synthesis of silver nanoparticles as effective SERS substrate.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020 Sep 1;200:110780. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110780. Epub 2020 May 26. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020. PMID: 32470683
-
β-Cyclodextrin coated SiO₂@Au@Ag core-shell nanoparticles for SERS detection of PCBs.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2015 Sep 7;17(33):21149-57. doi: 10.1039/c4cp04904g. Epub 2014 Dec 5. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2015. PMID: 25478906
-
Synthesis of a β-cyclodextrin-modified Ag film by the galvanic displacement on copper foil for SERS detection of PCBs.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2012 Jan 1;365(1):122-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2011.08.075. Epub 2011 Sep 14. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2012. PMID: 21968400
-
Rapid determination of marbofloxacin by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of silver nanoparticles modified by β-cyclodextrin.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2020 Mar 15;229:118009. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2019.118009. Epub 2019 Dec 31. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2020. PMID: 31927237
-
Surface-enhanced Raman scattering: realization of localized surface plasmon resonance using unique substrates and methods.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009 Aug;394(7):1747-60. doi: 10.1007/s00216-009-2762-4. Epub 2009 Apr 22. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009. PMID: 19384546 Review.
Cited by
-
β‑Cyclodextrin-Silver Nanoparticles Inclusion Complexes: Insights into Applications in Trace Level Detection (Light-Driven and Electrochemical Assays) and Antibacterial Activity.ACS Omega. 2025 Jun 4;10(23):23943-23956. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c03312. eCollection 2025 Jun 17. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40547675 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albrecht M.G., Creighton J.A. Anomalously intense Raman spectra of pyridine at a silver electrode. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1977;99:5215–5217. doi: 10.1021/ja00457a071. - DOI
-
- Jeanmaire D.L., Vanduyne R.P. Surface Raman spectroelectrochemistry. Part I. Heterocyclic, aromatic, and aliphatic amines adsorbed on the anodized silver electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1977;84:1–20. doi: 10.1016/S0022-0728(77)80224-6. - DOI
-
- Li Z.H., Hu J., Zhan Y.F., Shao Z.Y., Gao M.Y., Yao Q., Li Z., Sun S.W., Wang L.H. Coupling bifunctional nanozyme-mediated catalytic signal amplification and label-free SERS with immunoassays for ultrasensitive detection of pathogens in milk samples. Anal. Chem. 2023;95:6417–6424. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c00251. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

