Aptamer-Conjugated Multi-Quantum Dot-Embedded Silica Nanoparticles for Lateral Flow Immunoassay
- PMID: 39852105
- PMCID: PMC11763673
- DOI: 10.3390/bios15010054
Aptamer-Conjugated Multi-Quantum Dot-Embedded Silica Nanoparticles for Lateral Flow Immunoassay
Abstract
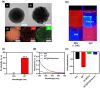
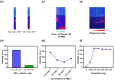
Lateral flow immunoassays (LFIAs) are widely used for their low cost, simplicity, and rapid results; however, enhancing their reliability requires the meticulous selection of ligands and nanoparticles (NPs). SiO2@QD@SiO2 (QD2) nanoparticles, which consist of quantum dots (QDs) embedded in a silica (SiO2) core and surrounded by an outer SiO2 shell, exhibit significantly higher fluorescence intensity (FI) compared to single QDs. In this study, we prepared QD2@PEG@Aptamer, an aptamer conjugated with QD2 using succinimidyl-[(N-maleimidopropionamido)-hexaethyleneglycol]ester, which is 130 times brighter than single QDs, for detecting carbohydrate antigen (CA) 19-9 through LFIA. For LFIA optimization, we determined the optimal conditions as a 1.0:2.0 × 10-2 ratio of polyethylene glycol (PEG) to aptamer by adjusting the amounts of PEG and aptamer, phosphate-buffered saline containing 0.5% Tween® 20 as a developing solution, and 0.15 μg NPs by setting the NP weight during development. Under these conditions, QD2@PEG@Aptamer selectively detected CA19-9, achieving a detection limit of 1.74 × 10-2 mg·mL-1. Moreover, FI remained stable for 10 days after detection. These results highlight the potential of QD2 and aptamer conjugation technology as a reliable and versatile sensing platform for various diagnostic applications.
Keywords: aptamer; carbohydrate antigen 19-9; lateral flow immunoassay; quantum dot.
Conflict of interest statement
H.S. Jung was employed by the company Zeus.
Figures

References
-
- Mahmoudi T., de la Guardia M., Baradaran B. Lateral flow assays towards point-of-care cancer detection: A review of current progress and future trends. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020;125:115842. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2020.115842. - DOI
-
- Shin M., Kim W., Yoo K., Cho H.-S., Jang S., Bae H.-J., An J., Lee J.-C., Chang H., Kim D.-E. Highly sensitive multiplexed colorimetric lateral flow immunoassay by plasmon-controlled metal–silica isoform nanocomposites: PINs. Nano Converg. 2024;11:42. doi: 10.1186/s40580-024-00449-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kim K., Kashefi-Kheyrabadi L., Joung Y., Kim K., Dang H., Chavan S.G., Lee M.-H., Choo J. Recent advances in sensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based lateral flow assay platforms for point-of-care diagnostics of infectious diseases. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021;329:129214. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2020.129214. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

