Identification of Potential Selective PAK4 Inhibitors Through Shape and Protein Conformation Ensemble Screening and Electrostatic-Surface-Matching Optimization
- PMID: 39852144
- PMCID: PMC11764389
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb47010029
Identification of Potential Selective PAK4 Inhibitors Through Shape and Protein Conformation Ensemble Screening and Electrostatic-Surface-Matching Optimization
Abstract
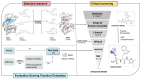
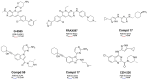
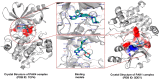
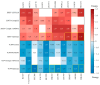
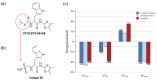
P21-activated kinase 4 (PAK4) plays a crucial role in the proliferation and metastasis of various cancers. However, developing selective PAK4 inhibitors remains challenging due to the high homology within the PAK family. Therefore, developing highly selective PAK4 inhibitors is critical to overcoming the limitations of existing inhibitors. We analyzed the structural differences in the binding pockets of PAK1 and PAK4 by combining cross-docking and molecular dynamics simulations to identify key binding regions and unique structural features of PAK4. We then performed screening using shape and protein conformation ensembles, followed by a re-evaluation of the docking results with deep-learning-driven GNINA to identify the candidate molecule, STOCK7S-56165. Based on this, we applied a fragment-replacement strategy under electrostatic-surface-matching conditions to obtain Compd 26. This optimization significantly improved electrostatic interactions and reduced binding energy, highlighting its potential for selectivity. Our findings provide a novel approach for developing selective PAK4 inhibitors and lay the theoretical foundation for future anticancer drug design.
Keywords: MM/GBSA; P21-activated kinases; electrostatic complementarity; molecular docking; molecular dynamics; selective inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Precise design of highly isoform-selective p21-activated kinase 4 inhibitors: computational insights into the selectivity mechanism through molecular dynamics simulation and binding free energy calculation.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2020 Aug;38(13):3825-3837. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2019.1664330. Epub 2019 Sep 15. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2020. PMID: 31490101
-
Strategy and validation of a structure-based method for the discovery of selective inhibitors of PAK isoforms and the evaluation of their anti-cancer activity.Bioorg Chem. 2019 Oct;91:103168. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103168. Epub 2019 Jul 30. Bioorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 31400553
-
In silico studies on p21-activated kinase 4 inhibitors: comprehensive application of 3D-QSAR analysis, molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations, and MM-GBSA calculation.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2020 Sep;38(14):4119-4133. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2019.1673823. Epub 2019 Oct 11. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2020. PMID: 31556340
-
P21-activated kinase 4--not just one of the PAK.Eur J Cell Biol. 2013 Apr-May;92(4-5):129-38. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2013.03.002. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Eur J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23642861 Review.
-
PAK4 signaling in health and disease: defining the PAK4-CREB axis.Exp Mol Med. 2019 Feb 12;51(2):1-9. doi: 10.1038/s12276-018-0204-0. Exp Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30755582 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

