Lipid Rafts in Signalling, Diseases, and Infections: What Can Be Learned from Fluorescence Techniques?
- PMID: 39852247
- PMCID: PMC11766618
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes15010006
Lipid Rafts in Signalling, Diseases, and Infections: What Can Be Learned from Fluorescence Techniques?
Abstract
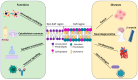
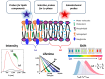
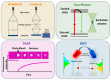
Lipid rafts are dynamic microdomains in the membrane, rich in cholesterol and sphingolipids, that are critical for biological processes like cell signalling, membrane trafficking, and protein organization. Their essential role is claimed in both physiological and pathological conditions, including cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and viral infections, making them a key area of research. Fluorescence-based approaches, including super-resolution fluorescence microscopy techniques, enable precise analysis of the organization, dynamics, and interactions of these microdomains, thanks also to the innovative design of appropriate fluorescent probes. Moreover, these non-invasive approaches allow for the study of live cells, facilitating the collection of quantitative data under physiologically relevant conditions. This review synthesizes the latest insights into the role of lipid rafts in biological and pathological processes and underscores how fluorescence techniques have advanced our understanding of these critical microdomains. The findings emphasize the pivotal role of lipid rafts in health and disease, providing a foundation for future research and potential therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: fluorescent probes; infections; lipid rafts; liquid-ordered phase; neurodegenerative disease; super resolution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

