Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia and the Kidney: Lessons from the URRAH Study
- PMID: 39852354
- PMCID: PMC11767115
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo15010011
Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia and the Kidney: Lessons from the URRAH Study
Abstract
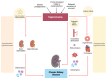
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a prevalent global health concern affecting approximately 850 million people worldwide, with a significant and rising mortality rate. CKD often coexists with hyperuricemia (HSUA), which is also increasingly common due to its association with hypertension, obesity, and diabetes. The interplay between hyperuricemia and CKD is complex; while in vitro studies and animal models support a role for uric acid mediating glomerular and tubule-interstitial damage, and HSUA has been shown to predict the onset and progression of CKD, the expectations of renal protection by the use of urate lowering treatment (ULT) are inconsistent. A significant challenge in managing asymptomatic HSUA in CKD patients lies in determining the appropriate SUA threshold values. Recent research, including the URRAH project, has sought to identify SUA cut-offs predictive of cardiovascular mortality, but these thresholds may vary depending on the severity of CKD. This variability complicates the establishment of universal guidelines for treating asymptomatic HSUA, leading to a lack of specific recommendations in clinical practice. In conclusion, while hyperuricemia is recognized as a prognostic factor for CKD and cardiovascular risk, more research is needed to refine the threshold values for SUA and to identify which patients may benefit from ULT. Stratification based on glomerular filtration rate may be necessary to tailor the treatments and improve outcomes in this population.
Keywords: cardiovascular risk; cut-offs; kidney disease; uric acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Foreman K.J., Marquez N., Dolgert A., Fukutaki K., Fullman N., McGaughey M., Pletcher M.A., Smith A.E., Tang K., Yuan C.-W., et al. Forecasting life expectancy, years of life lost, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 250 causes of death: Reference and alternative scenarios for 2016-40 for 195 countries and territories. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2018;392:2052–2090. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31694-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

