Optimizing Varicella Vaccination Strategy: A Study on Age and Dose Impacts on Antibody Levels
- PMID: 39852802
- PMCID: PMC11769036
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines13010023
Optimizing Varicella Vaccination Strategy: A Study on Age and Dose Impacts on Antibody Levels
Abstract
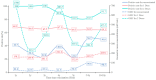
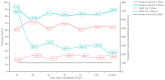
Seropositivity study of Varicella in Healthy Populations in Guangzhou, China. Infection with varicella-zoster virus (VZV) leads to skin and mucous membranes blisters and the complications can be life threatening. A seroepidemiological study conducted from 2020 to 2022 in Guangzhou, China, aimed to evaluate varicella antibody levels. We measured varicella antibody concentrations using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. A total of 3300 people were enrolled in the study. The mean varicella antibody level was 171.2 mIU/mL (95% CI: 158.9, 184.4), with an overall positivity rate of 67.00% (95% CI: 65.37, 68.60). The mean level of those positive subjective was 581.2 mIU/mL (95% CI: 552.3, 611.5). Varicella antibody levels were found to be influenced by age, vaccination dosage, and history of varicella infection. Antibody level increased with age and the number of vaccinations. The antibody induced by the varicella vaccine remained at protective levels for at least 6 years post-vaccination. We recommend two doses of the varicella vaccine for both children and adults and the integration of the varicella vaccine into the national routine immunization program.
Keywords: seroepidemiology; vaccination; varicella.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Varicella and herpes zoster vaccines: WHO position paper, June 2014. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 2014;89:265–287. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources