Acquired mutations in patients with relapsed/refractory CLL who progressed in the ALPINE study
- PMID: 39853273
- PMCID: PMC12008693
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2024014206
Acquired mutations in patients with relapsed/refractory CLL who progressed in the ALPINE study
Abstract
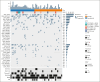
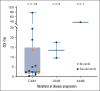
Some patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia who develop progressive disease (PD) during covalent Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor treatment acquire resistance mutations in BTK or PLCG2. Here, we report gene mutation data from paired baseline and PD peripheral blood samples from 52 patients (zanubrutinib, n = 24; ibrutinib, n = 28) who, at an early median follow-up of 25.7 months, progressed on zanubrutinib or ibrutinib treatment in ALPINE. No BTK mutations were observed at baseline; at PD, 8 patients (zanubrutinib, n = 5; ibrutinib, n = 3) acquired 17 BTK mutations, 82.4% (zanubrutinib, n = 11/14; ibrutinib, n = 3/3) at C481. Non-C481 mutations occurred in 12.5% (3/24) of zanubrutinib-treated patients (L528W: n = 2; cancer cell fraction [CCF] = 9.58% and 17.6%; A428D: n = 1; CCF = 37.03%). At baseline, 48 of 52 patients had ≥1 driver gene mutation(s), most frequently in NOTCH1 (n = 21), TP53 (n = 19), BRAF (n = 10), SF3B1 (n = 8), and ATM (n = 8). At PD, acquired mutations occurred in 1 zanubrutinib-treated patient (TP53, XPO1) and 5 ibrutinib-treated patients (TP53, n = 1 patient; SETD2, n = 1; SF3B1, n = 1; ASXL1, n = 2). Baseline driver gene mutations were not associated with development of BTK mutations, but patients with ≥2 baseline driver gene mutations were more likely to acquire BTK mutations at PD. The short treatment duration and a low BTK mutations incidence suggests that mechanisms other than BTK/PLCG2 mutations drive most early PD. This trial was registered at www.ClinicalTrials.gov as #NCT03734016.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: J.R.B. served as a consultant for AbbVie, Acerta/AstraZeneca, Alloplex Biotherapeutics, BeiGene, Galapagos NV, Genentech/Roche, Grifols Worldwide Operations, InnoCare Pharma Inc, iOnctura, Kite, Loxo@Lilly, Merck, Numab Therapeutics, Pfizer, and Pharmacyclics; and received research funding from BeiGene, Gilead, iOnctura, Loxo@Lilly, MEI Pharma, and TG Therapeutics. J.L. is employed and may own stock in BeiGene. B.E. served on advisory boards of Janssen, AbbVie, BeiGene, AstraZeneca, MSD, and Lilly; served on speakers bureaus of Roche, AbbVie, BeiGene, AstraZeneca, and MSD; received honoraria from Roche, AbbVie, BeiGene, AstraZeneca, and MSD; received research funding/grants from Janssen, Gilead, Roche, AbbVie, BeiGene, and AstraZeneca; and received travel expenses from BeiGene. N.L. served as a consultant for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Lilly, Genentech, Janssen, and Pharmacyclics; and received research funding from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Lilly, Genentech, Octapharma, Oncternal, MingSight, and TG Therapeutics. S.O. served as a consultant for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Lilly, Janssen, Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer, and Pharmacyclics; received research funding from BeiGene, Lilly, Pfizer, Pharmacyclics, and Regeneron; and reports membership in CLL Society (unpaid). C.S.T. received research funding from Janssen, AbbVie, and BeiGene; and received honoraria from Janssen, AbbVie, BeiGene, Lilly, and AstraZeneca. L.Q. reports consulting or advisory roles at BeiGene, Johnson & Johnson, Sanofi, and MSD; received research funding from BeiGene, Johnson & Johnson, and Pfizer; and served on the speakers bureaus of BeiGene, Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and Roche. R.H., Y.S., A.I., T.S., and A.C. are employed and may own stock in BeiGene. M.S. served as a consultant for AbbVie, Genentech, AstraZeneca, Genmab, Janssen, BeiGene, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), MorphoSys/Incyte, Kite Pharma, Lilly, Fate Therapeutics, Nurix, and Merck; received research funding from Mustang Bio, Genentech, AbbVie, BeiGene, AstraZeneca, Genmab, MorphoSys/Incyte, and Vincerx; holds stock in Koi Biotherapeutics; and reports employment at BMS (spouse).
Figures

References
-
- Skånland SS, Karlsen L, Taskén K. B cell signalling pathways—new targets for precision medicine in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Scand J Immunol. 2020;92(5) - PubMed
-
- Hallek M, Cheson BD, Catovsky D, et al. iwCLL guidelines for diagnosis, indications for treatment, response assessment, and supportive management of CLL. Blood. 2018;131(25):2745–2760. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

