Phase 2 Randomised Study of Bulevirtide as Monotherapy or Combined With Peg-IFNα-2a as Treatment for Chronic Hepatitis Delta
- PMID: 39853842
- PMCID: PMC11760647
- DOI: 10.1111/liv.70008
Phase 2 Randomised Study of Bulevirtide as Monotherapy or Combined With Peg-IFNα-2a as Treatment for Chronic Hepatitis Delta
Abstract
Background and aim: Bulevirtide (BLV) leads to beneficial virologic and biochemical responses when given alone to treat hepatitis delta virus (HDV) infection, which causes the most severe form of chronic viral hepatitis. We evaluated 48 weeks of BLV monotherapy, BLV + tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) and BLV + pegylated interferon alfa-2a (Peg-IFNα-2a), with 24-week follow-up.
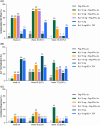
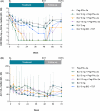
Methods: Ninety patients were enrolled into six arms of 15 each (A-F); 60 patients were included in the main randomisation (arms A-D), and 30 patients (arms E-F) were randomised to the extension phase: (A) Peg-IFNα-2a 180 μg once weekly (QW); (B) BLV 2 mg once daily (QD) + Peg-IFNα-2a 180 μg QW; (C) BLV 5 mg QD + Peg-IFNα-2a 180 μg QW; (D) BLV 2 mg QD; (E) BLV 10 mg QD + Peg-IFNα-2a 180 μg QW and (F) BLV 10 mg (5 mg twice daily) + TDF QD. The primary endpoint was undetectable HDV RNA at week (W)72.
Results: At W72, 53%, 27%, 7%, 7% and 33% of patients achieved undetectable HDV RNA in arms B, C, D, E and F, respectively, versus 0% in arm A. More arm B versus A patients had a > 1 log10 IU/mL decline in or loss of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) at W72 (p = 0.017), including four patients with loss of HBsAg. Bile acid elevations were dose-dependent and reversible following the completion of BLV treatment.
Conclusions: BLV combined with Peg-IFNα-2a was well tolerated and resulted in high rates of HDV RNA undetectability off-treatment.
Trial registration: NCT02888106.
Keywords: HDV; Hepcludex; Myrcludex B; bulevirtide; entry inhibitor; pegylated interferon alfa.
© 2025 The Author(s). Liver International published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Pietro Lampertico: Speaking bureau/advisory boards for AbbVie; Aligos Therapeutics; Antios Therapeutics; Bristol Myers Squibb; Eiger Biopharmaceuticals; Gilead Sciences Inc.; GSK; Janssen; Merck Sharp & Dohme; MYR Pharmaceuticals; Roche; and Vir Biotechnology. Vladimir Chulanov: Speaking bureau/advisory boards for AbbVie; Bristol Myers Squibb; Gilead Sciences Inc.; GSK; Hepatera; Merck Sharp & Dohme; R‐Pharm; and Roche. Maura Dandri: Research grants from Gilead Sciences Inc.; Hepatera; Humabs BioMed; and MYR GmbH; and consultancy for Gilead Sciences Inc. Jürgen Burhenne: Research grants from MYR GmbH. Antje Blank: Research grants from MYR GmbH. Sandra Ciesek: Speaker for Euroimmune, consultant for Novartis and research support from Roche and MYR GmbH. Ulf Dittmer: Reports consulting for AiCuris, Janssen, and Moderna. Qi An: Former employee of Gilead Sciences Inc. and owns stock. Dmitry Manuilov: Employee of Gilead Sciences Inc. and owns stock. Ben L. Da: Employee of Gilead Sciences Inc. and owns stock. John F. Flaherty: Employee of Gilead Sciences Inc. and owns stock. Stephan Urban: Reports consulting or speaking and/or research grants from Assembly Biosciences; Gilead Sciences Inc.; Hepatera; Humabs BioMed; MYR GmbH; PEPperPRINT GmbH; and Vir Biotechnology; and is a patent holder and inventor on patents protecting bulevirtide. Heiner Wedemeyer: Honoraria for speaking or consulting from Abbott; AbbVie; Boehringer Ingelheim; Bristol Myers Squibb; Eiger Biopharmaceuticals; Gilead Sciences Inc.; Janssen; Merck Sharp & Dohme; MYR GmbH; Novartis; Novira; Roche; Roche Diagnostics; Siemens; and Transgene; and research support from Abbott; Bristol Myers Squibb; Gilead Sciences Inc.; Novartis; Roche; and Roche Diagnostics. The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hughes S. A., Wedemeyer H., and Harrison P. M., “Hepatitis Delta Virus,” Lancet 378, no. 9785 (2011): 73–85. - PubMed

