A Clinical Practice-Based Comparison of Conventional and Individualized Dosing Strategies for Therapeutic Enoxaparin
- PMID: 39853909
- PMCID: PMC11760983
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.70039
A Clinical Practice-Based Comparison of Conventional and Individualized Dosing Strategies for Therapeutic Enoxaparin
Abstract
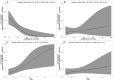
To understand differences in anti-factor-Xa levels produced by two different dosing strategies (conventional and individualized) for therapeutic enoxaparin in a cohort of hospital inpatients. A multicenter, retrospective cohort study over a two- and a half-year period for inpatients with stable renal function and on therapeutic enoxaparin. Anti-factor-Xa levels were taken 3-5 h after enoxaparin administration and a minimum of 48 h of dosing. The final analysis included 278 patients from five hospitals: conventional dosing was used for 141, while 137 were given an unconventional dose, that is, individualized for their renal function and weight. Out-of-range levels were frequent (35% to 40% of all inpatients). After adjustment for age, renal function, and body mass index (BMI), the conventional group was more likely to experience above-range levels (> 1.0 IU/mL; OR 2.50 [95% CI 1.38-4.56], p < 0.003) than the individualized group. Individualized dosing was independently associated with higher odds of a below-range anti-Xa level (< 0.5 IU/mL) compared to conventional dosing (OR 2.27 [95% CI 1.07-4.76], p = 0.03). Within the conventional group, above-range levels were significantly and independently associated with decreasing renal function (OR 0.97, 95% CI 0.96-0.99, p = 0.004) and with increasing BMI (OR 1.06, 95% CI 1.01-1.10, p = 0.02). No such associations were seen with an individualized approach. Clinical event rates were low and not different between groups (p > 0.24). Conventional therapeutic dosing of enoxaparin exposed people with obesity or renal impairment to more frequent above-range anti-factor-Xa levels; individualizing the dose could improve this but might expose people to subtherapeutic levels. More research is needed.
Keywords: enoxaparin; factor Xa; low‐molecular‐weight heparin.
© 2025 The Author(s). Pharmacology Research & Perspectives published by British Pharmacological Society and American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sanofi‐Aventis U.S. LLC , “Lovenox (Enoxaparin Sodium Injection) Package Insert,” Bridgewater, NJ: Sanofi‐Aventis U.S. LLC; 2007. In: Laval, Quebec: sanofi‐aventis Canada Inc.
-
- Frydman A. M., Bara L., Roux Y. H., Woler M., Chauliac F., and Samama M. M., “The Antithrombotic Activity and Pharmacokinetics of Enoxaparine, A Low Molecular Weight Heparin, in Humans Given Single Subcutaneous Doses of 20 to 80 Mg,” Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 28 (1988): 609–618. - PubMed
-
- Roberts G. W., Ibsen P. M., and Schioler C. T., “Modified Diet in Renal Disease Method Overestimates Renal Function in Selected Elderly Patients,” Age and Ageing 38 (2009): 698–703. - PubMed
-
- Barras M., “Anti‐Xa assays,” Australian Prescriber 36 (2013): 98–101.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical