Genome-wide identification and characterization of cation-proton antiporter (CPA) gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.) and their expression profiles in response to phytohormones
- PMID: 39854520
- PMCID: PMC11761165
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0317008
Genome-wide identification and characterization of cation-proton antiporter (CPA) gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.) and their expression profiles in response to phytohormones
Abstract
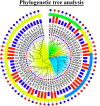
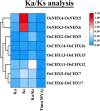
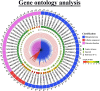
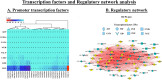
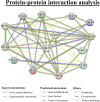
The cation-proton antiporter (CPA) superfamily plays pivotal roles in regulating cellular ion and pH homeostasis in plants. To date, the regulatory functions of CPA family members in rice (Oryza sativa L.) have not been elucidated. In this study, we use rice public data and information techniques, 29 OsCPA candidate genes were identified in the rice japonica variety (referred to as OsCPA) and phylogenetically categorized into K+ efflux antiporter (KEA), Na+/H+ exchanger (NHX), and cation/H+ exchanger (CHX) groups containing 4, 7, and 18 OsCPA genes. The OsCPA proteins were predominantly localized in the plasma membrane and unevenly scattered on 11 chromosomes. The structural analysis of OsCPA proteins revealed higher similarities within groups. Prediction of selection pressure, collinearity, and synteny analysis indicated that all duplicated OsCPA genes had undergone strong purifying selection throughout their evolution. The cis-acting regulatory elements (CAREs) analysis identified 56 CARE motifs responsive to light, tissue, hormones, and stresses. Additionally, 124 miRNA families were identified in the gene promoters, and OsNHX7 was targeted by the highest number of miRNAs (43 miRNAs). Gene Ontology analysis demonstrated the numerous functions of OsCPA genes associated with biological processes (57.14%), cellular components (7.94%), and molecular functions (34.92%). A total of 12 transcription factor families (TFFs), including 40 TFs were identified in gene promoters, with the highest numbers of TFFs (5TFFs) linked to OsCHX13, and OsCHX15. Protein-protein interaction analysis suggested maximum functional similarities between rice and Arabidopsis CPA proteins. Based on expression analysis, OsKEA1, OsKEA2, OsNHX3, and OsNHX7 were frequently expressed in rice tissues. Furthermore, OsNHX3, OsNHX4, OsNHX6, OsNHX7, OsCHX8, and OsCHX17 in abscisic acid, OsKEA1, OsNHX3, and OsCHX8 in gibberellic acid, OsKEA1, OsKEA3, OsNHX1, and OsNHX3 in indole-3-acetic acid treatment were demonstrated as potential candidates in response to hormone. These findings highlight potential candidates for further characterization of OsCPA genes, which may aid in the development of rice varieties.
Copyright: © 2025 Islam et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures










References
-
- Wang Y, Ying J, Zhang Y, Xu L, Zhang W, Ni M, et al.. Genome-Wide Identification and Functional Characterization of the Cation Proton Antiporter (CPA) Family Related to Salt Stress Response in Radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(21):8262. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218262 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

