Stable laser-acceleration of high-flux proton beams with plasma collimation
- PMID: 39856070
- PMCID: PMC11759682
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-56248-4
Stable laser-acceleration of high-flux proton beams with plasma collimation
Abstract
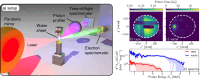
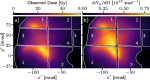
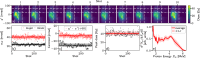
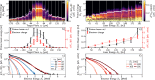
Laser-plasma acceleration of protons offers a compact, ultra-fast alternative to conventional acceleration techniques, and is being widely pursued for potential applications in medicine, industry and fundamental science. Creating a stable, collimated beam of protons at high repetition rates presents a key challenge. Here, we demonstrate the generation of multi-MeV proton beams from a fast-replenishing ambient-temperature liquid sheet. The beam has an unprecedentedly low divergence of 1° (≤20 mrad), resulting from magnetic self-guiding of the proton beam during propagation through a low density vapour. The proton beams, generated at a repetition rate of 5 Hz using only 190 mJ of laser energy, exhibit a hundred-fold increase in flux compared to beams from a solid target. Coupled with the high shot-to-shot stability of this source, this represents a crucial step towards applications.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Snavely, R. et al. Intense high-energy proton beams from Petawatt-laser irradiation of solids. Phys. Rev. Lett.85, 2945–2948 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Fuchs, J. et al. Laser-driven proton scaling laws and new paths towards energy increase. Nat. Phys.2, 48–54 (2005).
-
- Macchi, A., Borghesi, M. & Passoni, M. Ion acceleration by superintense laser-plasma interaction. Rev. Modern Phys.10.1103/RevModPhys.85.751 (2013).
-
- Daido, H., Nishiuchi, M. & Pirozhkov, A. S. Review of laser-driven ion sources and their applications. Rep. Prog. Phys.75, 056401 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Borghesi, M. et al. Electric field detection in laser-plasma interaction experiments via the proton imaging technique. Phys. Plasmas9, 2214–2220 (2002).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

