Identification of cold tumor induction-related markers in pancreatic cancer and the clinical implication of PCDH7
- PMID: 39856454
- PMCID: PMC11761478
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-025-06095-z
Identification of cold tumor induction-related markers in pancreatic cancer and the clinical implication of PCDH7
Abstract
Purpose: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is considered a "cold" tumor because the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) exhibits poor intratumoral T-cell infiltration. This study aimed to identify the marker genes associated with induction of cold TIME in PDAC cells.
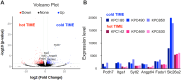
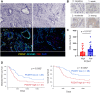
Methods: We orthotopically transplanted 10 primary cultures of PDAC derived from KrasG12D/+; Trp53R172H/+; Pdx-1-Cre (KPC) mice into immunocompetent mice and evaluated TIME by immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining of CD8. We divided primary cultures into two groups: cold TIME group with low CD8+ T-cell infiltration and a hot TIME group with high infiltration. RNA sequencing was performed to identify specific genes in the cold TIME group, and single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data was used for validation. IHC was performed to evaluate expressions in human PDAC samples.
Results: We identified six genes specific in PDAC cells to the cold TIME group by RNA sequencing; these were defined as "cold tumor induction-related genes". Human PDAC scRNA-seq data revealed that cold tumor induction-related genes were significantly and negatively correlated with the number of CD8+ T-cells (p = 0.0341). These genes included protocadherin 7 (PCDH7). High expression of PCDH7 significantly and negatively correlated with the number of CD8+ T-cells in scRNA-seq (p = 0.0474) and IHC (p = 0.0110) data using human PDAC samples. PCDH7 was an independent factor for poor prognosis in PDAC (overall survival: hazard ratio = 2.07, p = 0.0367).
Conclusion: PCDH7 is a prognostic marker associated with CD8+ T-cell infiltration for PDAC patients.
Keywords: CD8-positive T-lymphocytes; PCDH7 protein; Pancreatic cancer; Tumor escape; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Kyushu University (approval number: 22002-00). All animal experiments were conducted following the guidelines of the institutional animal committee of Kyushu University (approval number: A22-128 and A23-026). Consent to participate: Written informed consent was waived owing to the retrospective analysis of the study. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Chen DS, Mellman I (2013) Oncology meets immunology: the Cancer-Immunity cycle. Immunity 39:1–10. 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.07.012 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

