Automated AI-based image analysis for quantification and prediction of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis patients
- PMID: 39856708
- PMCID: PMC11762107
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-025-03117-9
Automated AI-based image analysis for quantification and prediction of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis patients
Abstract
Background: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a rare connective tissue disease associated with rapidly evolving interstitial lung disease (ILD), driving its mortality. Specific imaging-based biomarkers associated with the evolution of lung disease are needed to help predict and quantify ILD.
Methods: We evaluated the potential of an automated ILD quantification system (icolung®) from chest CT scans, to help in quantification and prediction of ILD progression in SSc-ILD. We used a retrospective cohort of 75 SSc-ILD patients to evaluate the potential of the AI-based quantification tool and to correlate image-based quantification with pulmonary function tests and their evolution over time.
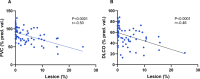
Results: We evaluated a group of 75 patients suffering from SSc-ILD, either limited or diffuse, of whom 30 presented progressive pulmonary fibrosis (PPF). The patients presenting PPF exhibited more extensive lesions (in % of total lung volume (TLV)) based on image analysis than those without PPF: 3.93 (0.36-8.12)* vs. 0.59 (0.09-3.53) respectively, whereas pulmonary functional test showed a reduction in Force Vital Capacity (FVC)(pred%) in patients with PPF compared to the others : 77 ± 20% vs. 87 ± 19% (p < 0.05). Modifications of FVC and diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide (DLCO) over time were correlated with longitudinal radiological ILD modifications (r=-0.40, p < 0.01; r=-0.40, p < 0.01 respectively).
Conclusion: AI-based automatic quantification of lesions from chest-CT images in SSc-ILD is correlated with physiological parameters and can help in disease evaluation. Further clinical multicentric validation is necessary in order to confirm its potential in the prediction of patient's outcome and in treatment management.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Computed tomography; Interstitial lung disease; Pulmonary function tests; Systemic sclerosis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was approved by the University Hospital of Liege Institutional Review Board (7072020000033). Consent to participate was waived considering the retrospective nature of the study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Clinical trial number: Not applicable. Competing interests: D.S. is an employee and shareholder of icometrix. S.VE is an employee of icometrix.
Figures



References
-
- Vonk MC, Smith V, Sfikakis PP, Cutolo M, Del Galdo F, Seibold JR. Pharmacological treatments for SSc-ILD: systematic review and critical appraisal of the evidence. Autoimmun Rev Neth. 2021;20:102978. - PubMed
-
- Fischer A, du Bois R. Interstitial lung disease in connective tissue disorders. Lancet (London, England). Engl; 2012;380:689–98. - PubMed
-
- O’Reilly S. Metabolic perturbations in systemic sclerosis. Curr Opin Rheumatol United States. 2022;34:91–4. - PubMed

