Glutamine and cancer: metabolism, immune microenvironment, and therapeutic targets
- PMID: 39856712
- PMCID: PMC11760113
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-024-02018-6
Glutamine and cancer: metabolism, immune microenvironment, and therapeutic targets
Abstract
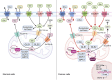
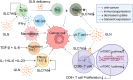
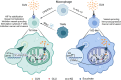
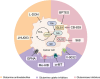
Glutamine is the most abundant amino acid in human serum, and it can provide carbon and nitrogen for biosynthesis, which is crucial for proliferating cells. Moreover, it is widely known that glutamine metabolism is reprogrammed in cancer cells. Many cancer cells undergo metabolic reprogramming targeting glutamine, increasing its uptake to meet their rapid proliferation demands. An increasing amount of study is being done on the particular glutamine metabolic pathways in cancer cells.Further investigation into the function of glutamine in immune cells is warranted given the critical role these cells play in the fight against cancer. Immune cells use glutamine for a variety of biological purposes, including the growth, differentiation, and destruction of cancer cells. With the encouraging results of cancer immunotherapy in recent years, more investigation into the impact of glutamine metabolism on immune cell function in the cancer microenvironment could lead to the discovery of new targets and therapeutic approaches.Oral supplementation with glutamine also enhances the immune capabilities of cancer patients, improves the sensitivity to chemotherapy and radiotherapy, and improves prognosis. The unique metabolism of glutamine in cancer cells, its function in various immune cells, the impact of inhibitors of glutamine metabolism, and the therapeutic use of glutamine supplements are all covered in detail in this article.
Keywords: Cancer; Glutaminase inhibitors; Glutamine antimetabolites; Glutamine metabolism; Immune cells.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- “On the Origin of Cancer Cells | Science.” Accessed: Aug. 24, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.123.3191.309?url_ver=Z39.88-.... - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82203377/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82473238/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- LQ22H160036/Zhejiang natural science foundation of China
- LY24H160022/Zhejiang natural science foundation of China
- JBZX-202007/Research Center for Lung Tumor Diagnosis and Treatment of Zhejiang Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

