The role of programmed cell death in organ dysfunction induced by opportunistic pathogens
- PMID: 39856779
- PMCID: PMC11761187
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-025-05278-x
The role of programmed cell death in organ dysfunction induced by opportunistic pathogens
Abstract
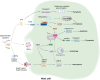
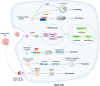
Sepsis is a life-threatening condition resulting from pathogen infection and characterized by organ dysfunction. Programmed cell death (PCD) during sepsis has been associated with the development of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS), impacting various physiological systems including respiratory, cardiovascular, renal, neurological, hematological, hepatic, and intestinal systems. It is well-established that pathogen infections lead to immune dysregulation, which subsequently contributes to MODS in sepsis. However, recent evidence suggests that sepsis-related opportunistic pathogens can directly induce organ failure by promoting PCD in parenchymal cells of each affected organ. This study provides an overview of PCD in damaged organ and the induction of PCD in host parenchymal cells by opportunistic pathogens, proposing innovative strategies for preventing organ failure in sepsis.
Keywords: Opportunistic pathogens; Organ failure; Programmed cell death; Sepsis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med. 2017;43(3):304–77. - PubMed
-
- Kaukonen KM, Bailey M, Suzuki S, et al. Mortality related to severe sepsis and septic shock among critically ill patients in Australia and New Zealand, 2000–2012. JAMA. 2014;311(13):1308–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2022YFC2304601/National Key R&D Program of China from the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China
- 2021YFC2500801/National Key R&D Program of China from the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China
- 2021-I2M-1-062/Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (CAMS) Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

