Impact of Microwave Time on the Structure and Functional Properties of Glycosylated Soy 7S Globulins
- PMID: 39856821
- PMCID: PMC11764794
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14020151
Impact of Microwave Time on the Structure and Functional Properties of Glycosylated Soy 7S Globulins
Abstract
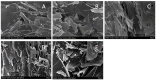
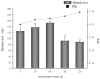
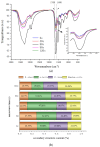
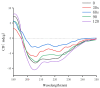
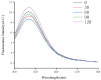
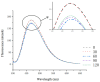
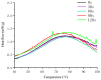
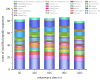
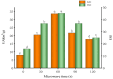
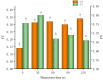
This study examined the effects of varying microwave treatment durations (0-120 s) on the structural and functional properties of glycosylated soybean 7S protein. The results indicated that microwaving for 60 s significantly altered the structure of 7S, resulting in a more ordered protein configuration. The treated protein exhibited the largest particle size (152.3 nm), lowest polydispersity index (0.248), highest α-helix content (47.86%), and lowest β-sheet, β-turn, and random coil contents (12.33%, 16.07%, and 22.41%, respectively). It also showed the lowest endogenous fluorescence and surface hydrophobicity, and the highest thermal denaturation temperature (76.8 °C). Additionally, microwaving for ≤90 s led to increased peptide modifications, with carbamylation and deamidation being the most prevalent. A microwave treatment time of 60 s also notably enhanced the functional properties of glycosylated soybean 7S protein, optimizing water-holding capacity (6.060 g/g), emulsification activity, and stability (45.191 m2/g and 33.63 min). The foaming capacity was second only to the 120 s treatment (32% at 60 s versus 34% at 120 s), though the oil-holding capacity (22.73 g/g) and foaming stability (33.42%) were significantly lower than those of the controls. Microwave treatment durations exceeding or below 60 s led to the structural disintegration of the protein, diminishing most of its functional properties. This study explores the mechanism of how microwave processing time affects the structure and functional properties of glycosylated soybean 7S protein and identifies 60 s as the optimal microwave processing time. It meets the demands for healthy and delicious food in home cooking, providing scientific evidence for using microwave processing technology to enhance the nutritional value and quality of food.
Keywords: food industry; functional properties; glycosylation; microwave heating; soy 7S globulin; structural properties.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structure and Functional Properties of Proteins from Different Soybean Varieties as Affected by the 11S/7S Globulin Ratio.Foods. 2025 Feb 23;14(5):755. doi: 10.3390/foods14050755. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40077457 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of High-Intensity Ultrasound Pretreatment on the Properties of the Transglutaminase (TGase)-Induced β-Conglycinin (7S) Gel.Foods. 2023 May 17;12(10):2037. doi: 10.3390/foods12102037. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37238854 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of electric field intensity regulation on protein aggregation behaviour and foaming property of soybean 7S globulin.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Sep 1;248:125784. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125784. Epub 2023 Jul 13. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37451384
-
Different interactions driving the binding of soy proteins (7S/11S) and flavonoids (quercetin/rutin): Alterations in the conformational and functional properties of soy proteins.Food Chem. 2022 Dec 1;396:133685. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133685. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Food Chem. 2022. PMID: 35843004
-
Structural and functional analysis of various globulin proteins from soy seed.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2015;55(11):1491-502. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2012.700340. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2015. PMID: 24915310 Review.
Cited by
-
Legume Proteins in Food Products: Extraction Techniques, Functional Properties, and Current Challenges.Foods. 2025 May 4;14(9):1626. doi: 10.3390/foods14091626. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40361707 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang Q., Wu H., Yan W., Pang T., Fu M. Advances in the physicochemical properties of soybean 7S and 11S globulins and their modified modification. Food Ferment. Ind. 2022;48:324–335.
-
- Huang S., Huang M., Dong X. Advanced Glycation End Products in Meat during Processing and Storage: A Review. Food Rev. Int. 2023;39:1716–1732. doi: 10.1080/87559129.2021.1936003. - DOI
-
- Jiang L., Zheng K., Hou X., Darwish I.A. Maillard-induced chia seed mucilage glycation-modified whey protein isolate conjugate: Insights from functional properties and untargeted metabolomics. Food Biosci. 2025;63:105692. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2024.105692. - DOI
-
- Luan H., Hua X., Dai S., Jia X., Yin L. Application of Wet Glycosylation Modified Soybean Protein Isolate inHypo-allergenic Chiba Tofu. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2024;45:59–66.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

