Application of Convolutional Neural Networks and Recurrent Neural Networks in Food Safety
- PMID: 39856912
- PMCID: PMC11764514
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14020247
Application of Convolutional Neural Networks and Recurrent Neural Networks in Food Safety
Abstract
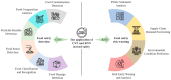
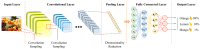
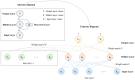
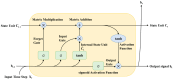
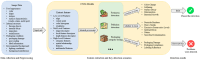
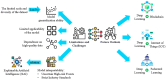
This review explores the application of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) in food safety detection and risk prediction. This paper highlights the advantages of CNNs in image processing and feature recognition, as well as the powerful capabilities of RNNs (especially their variant LSTM) in time series data modeling. This paper also makes a comparative analysis in many aspects: Firstly, the advantages and disadvantages of traditional food safety detection and risk prediction methods are compared with deep learning technologies such as CNNs and RNNs. Secondly, the similarities and differences between CNNs and fully connected neural networks in processing image data are analyzed. Furthermore, the advantages and disadvantages of RNNs and traditional statistical modeling methods in processing time series data are discussed. Finally, the application directions of CNNs in food safety detection and RNNs in food safety risk prediction are compared. This paper also discusses combining these deep learning models with technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, and federated learning to improve the accuracy and efficiency of food safety detection and risk warning. Finally, this paper mentions the limitations of RNNs and CNNs in the field of food safety, as well as the challenges in the interpretability of the model, and suggests the use of interpretable artificial intelligence (XAI) technology to improve the transparency of the model.
Keywords: convolutional neural networks; deep learning; food safety; long short-term memory; recurrent neural networks.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Weston M., Geng S., Chandrawati R. Food sensors: Challenges and opportunities. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021;6:2001242. doi: 10.1002/admt.202001242. - DOI
-
- Domínguez I., Frenich A.G., Romero-González R. Mass spectrometry approaches to ensure food safety. Anal. Methods. 2020;12:1148–1162. doi: 10.1039/C9AY02681A. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

