Microalga Nannochloropsis gaditana as a Sustainable Source of Bioactive Peptides: A Proteomic and In Silico Approach
- PMID: 39856918
- PMCID: PMC11765504
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14020252
Microalga Nannochloropsis gaditana as a Sustainable Source of Bioactive Peptides: A Proteomic and In Silico Approach
Abstract
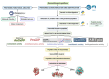
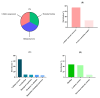
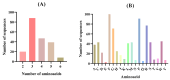
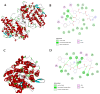
The impact of the world's growing population on food systems and the role of dietary patterns in the management of non-communicable diseases underscore the need to explore sustainable and dietary protein sources. Although microalgae have stood out as alternative sources of proteins and bioactive peptides, some species such as Nannochloropsis gaditana remain unexplored. This study aimed to characterize N. gaditana's proteome and evaluate its potential as a source of bioactive peptides by using an in silico approach. A total of 1955 proteins were identified and classified into functional groups of cellular components, molecular functions, and biological processes. In silico gastrointestinal digestion of identified proteins demonstrated that 202 hydrophobic and low-molecular-size peptides with potential bioactivity were released. Among them, 27 exhibited theorical antioxidant, antihypertensive, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, and/or antimicrobial activities. Seven of twenty-seven peptides showed ≥20% intestinal absorption, suggesting potential systemic effects, while the rest could act at local level. Molecular docking demonstrated strong affinities with key enzymes such as MPO, ACE, and DPPIV. Resistance to the digestion, capacity to be absorbed, and multifunctionality were demonstrated for peptide FIPGL. This study highlights N. gaditana's potential as a sustainable source of novel potential bioactive peptides with promising local and systemic biological effects.
Keywords: Nannochloropsis sp.; functional analysis; in silico digestion; microalgae; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Valorisation of the microalgae Nannochloropsis gaditana biomass by proteomic approach in the context of circular economy.J Proteomics. 2019 Feb 20;193:239-242. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2018.10.015. Epub 2018 Oct 29. J Proteomics. 2019. PMID: 30385413
-
In Vivo Nutritional Assessment of the Microalga Nannochloropsis gaditana and Evaluation of the Antioxidant and Antiproliferative Capacity of Its Functional Extracts.Mar Drugs. 2022 May 11;20(5):318. doi: 10.3390/md20050318. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35621969 Free PMC article.
-
Development of New Antiproliferative Compound against Human Tumor Cells from the Marine Microalgae Nannochloropsis gaditana by Applied Proteomics.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 24;22(1):96. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010096. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33374179 Free PMC article.
-
Edible Insects as a Novel Source of Bioactive Peptides: A Systematic Review.Foods. 2023 May 17;12(10):2026. doi: 10.3390/foods12102026. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37238844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of the "Applied Proteomics" Concept for Biotechnology Applications in Microalgae: Example of the Proteome Data in Nannochloropsis gaditana.Mar Drugs. 2021 Dec 29;20(1):38. doi: 10.3390/md20010038. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 35049892 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unlocking the Functional and Nutritional Potential of Microalgae Proteins in Food Systems: A Narrative Review.Foods. 2025 Apr 26;14(9):1524. doi: 10.3390/foods14091524. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40361607 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Budreviciute A., Damiati S., Sabir D.K., Onder K., Schuller-Goetzburg P., Plakys G., Katileviciute A., Khoja S., Kodzius R. Management and Prevention Strategies for Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) and Their Risk Factors. Front. Public Health. 2020;8:574111. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.574111. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

