Factors Influencing the Development of Metachronous Fractures in Patients with Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures Treated with Conservative Management or Vertebroplasty
- PMID: 39857044
- PMCID: PMC11765220
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15020160
Factors Influencing the Development of Metachronous Fractures in Patients with Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures Treated with Conservative Management or Vertebroplasty
Abstract
Objectives: We aimed to analyze potential predictors for the development of metachronous fractures (MFs) after osteoporotic vertebral fractures (OVFs), with particular focus on radiological variables obtained at initial X-rays and computed tomography (CT) examinations, treatment applied (conservative management [CM] versus percutaneous vertebroplasty [PV]), and fractures located at the thoracolumbar junction (T11-L2). Methods: We conducted a two-center, observational retrospective study, including patients with single-level OVFs treated with CM or VP. We collected socio-demographic, radiological and treatment-related variables. We performed descriptive and contrastive bivariate analyses based on the presence of MFs and univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses to obtain adjusted and crude odds ratios (aOR and cOR, respectively) for predicting MFs. Finally, we performed receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve analyses to determine the discriminative power of the models obtained. Results: Of the 90 patients included, 20 (22.2%) developed one or more MFs (15 in CM and 5 in PV groups, respectively; p = 0.037). The treatment group (aOR for PV, 0.087; 95%CI, 0.015-0.379), presence of intravertebral cleft (aOR, 5.62; 95%CI, 1.84-19.2) and difference in posterior height loss between X-rays and CT (aOR, 0.926; 95%CI, 0.856-0.992) were identified as significant predictors for MFs, while Genant's numerical classification showed a trend toward significance (aOR, 1.97; 95%CI, 0.983-4.19; p = 0.064). A multivariate model combining these four variables showed optimal fitting and correctly discriminated over 80% of cases (AUC, 0.828; 95%CI, 0.725-0.930). Factors associated with MFs in thoracolumbar junction OVFs were intravertebral cleft, CM, posterior height loss in CT, and DGOU OF3 fractures. Conclusions: The presence of intravertebral cleft, a difference in posterior height loss between X-rays and CT equal to or lower than 2.4%, higher grades of Genant's numerical classification, and application of CM instead of PV are predictors of MFs. These findings improve our understanding of the factors involved in the development of MFs, but they need to be validated prospectively.
Keywords: conservative management; fracture; osteoporosis; percutaneous vertebroplasty; risk factor; spine.
Conflict of interest statement
The first and senior authors host a special issue in
Figures
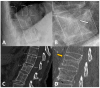
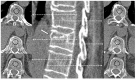
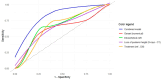

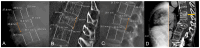
References
-
- Yamauchi K., Adachi A., Kameyama M., Murakami M., Sato Y., Kato C., Kato T. A Risk Factor Associated with Subsequent New Vertebral Compression Fracture after Conservative Therapy for Patients with Vertebral Compression Fracture: A Retrospective Observational Study. Arch. Osteoporos. 2020;15:1–12. doi: 10.1007/s11657-019-0679-x. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

