A Narrative Review of Biomarkers and Imaging in the Diagnosis of Acute Aortic Syndrome
- PMID: 39857067
- PMCID: PMC11765216
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15020183
A Narrative Review of Biomarkers and Imaging in the Diagnosis of Acute Aortic Syndrome
Abstract
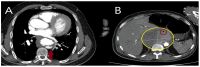
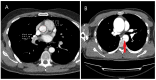
Acute aortic syndrome (AAS) encompasses a range of life-threatening conditions, including classical dissection, intramural hematoma, and penetrating aortic ulcer. Each of these conditions presents distinct clinical characteristics and carries the potential to progress to rupture. Because AAS can be asymptomatic or present with diverse symptoms, its diagnosis requires clinical evaluation, risk scoring, and biomarkers such as D-dimer (DD), C-reactive protein (CRP), homocysteine, natriuretic peptides (BNP), and imaging modalities like computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and echocardiography. While this review primarily focuses on widely used and clinically accessible biomarkers and imaging techniques, it also discusses alternative biomarkers proposed for diagnostic use. Although CT remains the gold standard for diagnosis, biomarkers facilitate rapid risk stratification, complementing imaging techniques. Emerging technologies, such as metabolomics, are reshaping diagnostic algorithms. Despite advances in diagnostic methods, challenges such as misdiagnosis and missed diagnoses persist. Ongoing research into novel biomarkers and innovative imaging techniques holds promise for improving diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes.
Keywords: D-dimer; acute aortic syndrome; aortic dissection; artificial intelligence; biomarkers; computed tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
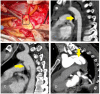
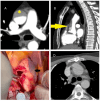
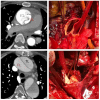
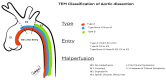
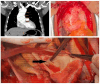
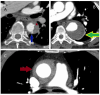
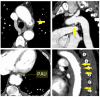
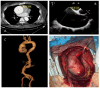
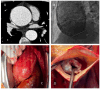
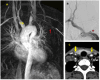
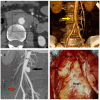
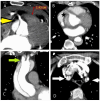
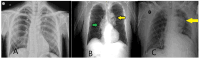
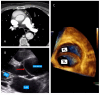
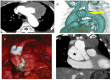
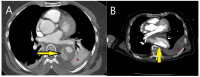
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

