Osteoprotegerin as an Emerging Biomarker of Carotid Artery Stenosis? A Scoping Review with Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 39857103
- PMCID: PMC11764218
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15020219
Osteoprotegerin as an Emerging Biomarker of Carotid Artery Stenosis? A Scoping Review with Meta-Analysis
Abstract
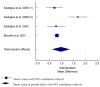
Objective: In developed countries, stroke is the fifth cause of death, with a high mortality rate, and with recovery to normal neurological function in one-third of survivors. Atherosclerotic occlusive disease of the extracranial part of the internal carotid artery and related embolic complications are common preventable causes of ischemic stroke (IS), attributable to 7-18% of all first-time cases. Osteoprotegerin (OPG), a soluble member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) superfamily, is considered a modulator of vascular calcification linked to vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and collagen production in atherosclerotic plaques. Therefore, OPG emerges as a potential biomarker (BM) of calcified carotid plaques and carotid artery stenosis (CAS). Methods: We performed a literature search of PubMed on OPG in CAS and atherosclerosis published until 2024. Results: Increased levels of serum OPG were reported in both patients with symptomatic and asymptomatic CAS, and higher values were observed in those with unstable atherosclerotic plaques. Notably, increased OPG levels were observed regardless of the location of atherosclerosis, including coronary and other peripheral arteries. In addition, chronic kidney disease, the most significant confounder disturbing the association between vascular damage and circulating OPG levels, decreases the usefulness of OPG as a BM in CAS. Conclusions: Osteoprotegerin may be considered an emerging BM of global rather than cerebrovascular atherosclerosis. Its diagnostic significance in identifying patients with asymptomatic CAS and their monitoring is limited.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; carotid stenosis; osteoprotegerin; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Elevated Circulating Osteoprotegerin Levels in the Plasma of Hemodialyzed Patients With Severe Artery Calcification.Ther Apher Dial. 2018 Oct;22(5):519-529. doi: 10.1111/1744-9987.12681. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Ther Apher Dial. 2018. PMID: 29974642
-
Assessment of the genetic effects of polymorphisms in the osteoprotegerin gene, TNFRSF11B, on serum osteoprotegerin levels and carotid plaque vulnerability.Stroke. 2011 Nov;42(11):3022-8. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.619288. Epub 2011 Sep 8. Stroke. 2011. PMID: 21903966
-
Bone marrow- or vessel wall-derived osteoprotegerin is sufficient to reduce atherosclerotic lesion size and vascular calcification.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Nov;33(11):2491-500. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301755. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23990207
-
[Osteoprotegerin as a marker of atherosclerosis and a prognostic factor in stroke].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2015 Dec 31;69:1505-11. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2015. PMID: 27259222 Review. Polish.
-
Osteoprotegerin and kidney disease.J Nephrol. 2014 Dec;27(6):607-17. doi: 10.1007/s40620-014-0092-x. Epub 2014 Apr 23. J Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24756971 Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

