Lipid Oxidation at the Crossroads: Oxidative Stress and Neurodegeneration Explored in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 39857412
- PMCID: PMC11762898
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox14010078
Lipid Oxidation at the Crossroads: Oxidative Stress and Neurodegeneration Explored in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
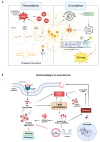
Lipid metabolism plays a critical role in maintaining cellular integrity, especially within the nervous system, where lipids support neuronal structure, function, and synaptic plasticity. However, this essential metabolic pathway is highly susceptible to oxidative stress, which can lead to lipid peroxidation, a damaging process induced by reactive oxygen species. Lipid peroxidation generates by-products that disrupt many cellular functions, with a strong impact on proteostasis. In this review, we explore the role of lipid oxidation in protein folding and its associated pathological implications, with a particular focus on findings in neurodegeneration from Caenorhabditis elegans studies, an animal model that remains underutilized. Additionally, we highlight the effectiveness of different methodologies applied in this nematode to deepen our understanding of this intricate process. In the nervous system of any animal, including mammals and invertebrates, lipid oxidation can disturb the delicate balance of cellular homeostasis, leading to oxidative stress, the build-up of toxic by-products, and protein misfolding, key factors in neurodegenerative diseases. This disruption contributes to the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, or Huntington's disease. The findings from Caenorhabditis elegans studies offer valuable insights into these complex processes and highlight potential avenues for developing targeted therapies to mitigate neurodegenerative disease progression.
Keywords: C. elegans; lipid metabolism; lipid oxidation; neurodegenerative disorders; protein misfolding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Paulsen J.S., Nance M., Kim J., Carlozzi N., Panegyres P., Erwin C., Goh A., McCusker E., Williams J.K. A Review of Quality of Life after Predictive Testing for and Earlier Identification of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013;110:2–28. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.08.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- van Lonkhuizen P.J.C., Frank W., Heemskerk A.-W., van Duijn E., de Bot S.T., Mühlbäck A., Landwehrmeyer G.B., Chavannes N.H., Meijer E., the HEALTHE-RND consortium Quality of Life, Health-Related Quality of Life, and Associated Factors in Huntington’s Disease: A Systematic Review. J. Neurol. 2023;270:2416–2437. doi: 10.1007/s00415-022-11551-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Leite Silva A.B.R., Gonçalves de Oliveira R.W., Diógenes G.P., de Castro Aguiar M.F., Sallem C.C., Lima M.P.P., de Albuquerque Filho L.B., Peixoto de Medeiros S.D., Penido de Mendonça L.L., de Santiago Filho P.C., et al. Premotor, Nonmotor and Motor Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease: A New Clinical State of the Art. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023;84:101834. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2022.101834. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

