A Multi- Mediation Analysis on the Impact of Social Media and Internet Addiction on University and High School Students' Mental Health Through Social Capital and Mindfulness
- PMID: 39857510
- PMCID: PMC11764769
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph22010057
A Multi- Mediation Analysis on the Impact of Social Media and Internet Addiction on University and High School Students' Mental Health Through Social Capital and Mindfulness
Abstract
Introduction: Social media addiction (SMA) and internet addiction (IA) are increasingly prevalent, impacting mental health (MH) globally. This study investigates the mediating roles of mindfulness and social capital (SC) in the relationship between SMA, IA, and MH among Ethiopian high school and university students, contributing to the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 3 of good health and well-being.
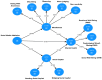
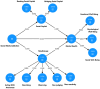
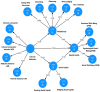
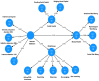
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted with 1160 university and 1473 high school students in Dessie, Ethiopia. Participants completed validated questionnaires assessing SMA, IA, mindfulness, SC, and MH. Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) with a multi- mediation Model (SMM) was used to examine the hypothesized relationships.
Results: SEM revealed that both SMA and IA had a direct negative effect on mindfulness, SC, and MH in in both high school and university students. Notably, mindfulness and SC significantly and positively predicted MH, indicating their protective role against the negative effects of SMA and IA. Furthermore, both mindfulness or SC fully or partially mediated the relationship between SMA, IA, and MH, highlighting their crucial role in explaining the association.
Conclusions: This study provides evidence for the crucial roles of mindfulness and SC in buffering the negative effects of SMA and IA on MH among Ethiopian students. The findings highlight the need for educational and health interventions that foster mindfulness and SC to enhance student mental health and promote a healthy digital environment. These results offer valuable insights for educators, health professionals, and policymakers in Ethiopia and other developing countries facing similar challenges.
Keywords: internet addiction; mental health; mindfulness; multi- mediation analysis; social capital; social media addiction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The relationship between family functioning and social media addiction among university students: a moderated mediation model of depressive symptoms and peer support.BMC Psychol. 2024 Jun 10;12(1):341. doi: 10.1186/s40359-024-01818-2. BMC Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38858753 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the mediating role of insomnia on the nexus between social media addiction and mental health among university students.Sci Rep. 2025 May 22;15(1):17872. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-03163-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40404911 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of social suspicion on social media addiction among Chinese college students: A moderated mediation model.PLoS One. 2025 May 21;20(5):e0323474. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323474. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40397848 Free PMC article.
-
The association between school bullying and internet addiction among adolescents: a moderated mediation model.Front Public Health. 2025 Mar 27;13:1502726. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1502726. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40213425 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Problematic TikTok Use and Mental Health Issues: A Systematic Review of Empirical Studies.J Prim Care Community Health. 2025 Jan-Dec;16:21501319251327303. doi: 10.1177/21501319251327303. Epub 2025 Mar 19. J Prim Care Community Health. 2025. PMID: 40105453 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Parallel Mediation Model of Career Adaptability, Career Self-Efficacy, and Future Career Choice Among University Students: The Role of Basic Psychological Needs Satisfaction and Mindfulness.Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2025 Mar 26;15(4):47. doi: 10.3390/ejihpe15040047. Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2025. PMID: 40277864 Free PMC article.
-
Online Captive: The Impact of Social Media Addiction on Depression and Anxiety-An SEM Approach to the Mediating Role of Self-Esteem and the Moderating Effects of Age and Professional Status.Behav Sci (Basel). 2025 Apr 7;15(4):481. doi: 10.3390/bs15040481. Behav Sci (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40282102 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Moderating Effect of Language Attitude in the Interplay Among Social Media Addiction, Social Pain and Internet Trolling in College Students.Behav Sci (Basel). 2025 Apr 27;15(5):586. doi: 10.3390/bs15050586. Behav Sci (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40426364 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jin Y., Austin L.L. Social Media and Crisis Communication. Routledge; New York, NY, USA: 2022. - DOI
-
- Carr C.T., Hayes R.A. Social media: Defining, developing, and divining. Atl. J. Commun. 2015;23:46–65. doi: 10.1080/15456870.2015.972282. - DOI
-
- Fathi A., Sadeghi S., Maleki Rad A.A., Sharifi Rahnmo S., Rostami H., Abdolmohammadi K. The role of cyberspace uses on lifestyle promoting health and coronary anxiety in young people. Iran. J. Psychiatry Clin. Psychol. 2020;26:332–347. doi: 10.32598/ijpcp.26.3415.1. - DOI
-
- Tsang E.W., Yuen C.C.Y., Lau J.C.M., Ma V.W.K., Wat M.T.H., Yu J.Y.Y., Privitera A.J., Chung R.C.K., Chan C.C.H. Influences of Lifestyle Profiles and Problematic Internet Use on Mental Distress in University Students. Psychol. Studies. 2024;69:81–91. doi: 10.1007/s12646-023-00766-y. - DOI
-
- Zhao L. Social Media Addiction and Its Impact on College Students’ Academic Performance: The Mediating Role of Stress. Asia-Pac. Educ. Res. 2023;32:81–90. doi: 10.1007/s40299-021-00635-0. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

