Using a Hand-Held Icterometer to Screen for Neonatal Jaundice: Validation, Feasibility, and Acceptability of the Bili-RulerTM in Kumasi, Ghana
- PMID: 39857549
- PMCID: PMC11764747
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph22010096
Using a Hand-Held Icterometer to Screen for Neonatal Jaundice: Validation, Feasibility, and Acceptability of the Bili-RulerTM in Kumasi, Ghana
Abstract
Background: Neonatal jaundice (NNJ) remains a leading cause of newborn mortality in much of sub-Saharan Africa. We sought to examine the validity of using a hand-held icterometer as a screening tool to determine which newborns need further assessment. Additionally, we sought to assess the feasibility of its use among mothers.
Methods: We recruited and trained healthcare workers at one large district hospital in Ghana to use a hand-held icterometer known as the Bili-RulerTM. We recruited mothers of 341 newborns aged 0 to 2 weeks at the same hospital. Mothers watched a standardized training video, after which they blanched the skin of the newborn's nose and compared it with the yellow shades numbered one to six on the icterometer. Each newborn was also assessed with a transcutaneous bilirubin meter (TCB). Research assistants and health care workers screened the same newborns, recorded their scores separately, and were blinded to each other's readings. In the second phase of this study, we recruited 100 new mothers to take the Bili-Ruler home with them, instructing them to check their newborns twice daily. We interviewed them 1-2 weeks later to determine the acceptability and feasibility of its use.
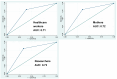
Results: Out of 341 newborns screened, 20 had elevated TCB indicative of hyperbilirubinemia. Healthcare workers' Bili-Ruler ratings had a strong and significant correlation with TCB scores, as did the ratings of researchers and mothers. When comparing Bili-Ruler scores against TCB, sensitivity across all three raters was 80% (95% CI 75.6-84.3), specificity ranged from 61.1% (healthcare providers) to 66.7% (researchers), positive predictive value ranged from 11.4% (healthcare providers) to 13.0% (researchers), and negative predictive value was 98.0% or higher across all raters. Area under the ROC curve ranged from 0.71 for healthcare providers to 0.73 for researchers. Mothers AUC was 0.72. In terms of acceptability and feasibility, the Bili-Ruler was widely accepted by the mothers and family. In total, 98% of mothers reported using it, and 90.8% used it 3 or more days in the first week after birth. Moreover, 89.8% used it more than twice per day.
Conclusions: A hand-held, low-tech icterometer is an important potential mechanism for improving early jaundice identification in low-resource settings. Further studies using larger sample sizes with a higher prevalence of hyperbilirubinemia are warranted.
Keywords: Bili-Ruler; Ghana; Sub-Saharan Africa; hyperbilirubinemia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bhutani V.K., Zipursky A., Blencowe H., Khanna R., Sgro M., Ebbesen F., Bell J., Mori R., Slusher T.M., Fahmy N., et al. Neonatal hyperbilirubinemia and Rhesus disease of the newborn: Incidence and impairment estimates for 2010 at regional and global levels. Pediatr. Res. 2013;74:86–100. doi: 10.1038/pr.2013.208. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- IHME. Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 (GBD 2019) Data Resources|GHDx. [(accessed on 17 October 2024)]. Available online: https://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

