SSL5-AnxA5 Fusion Protein Constructed Based on Human Atherosclerotic Plaque scRNA-Seq Data Preventing the Binding of Apoptotic Endothelial Cells, Platelets, and Inflammatory Cells
- PMID: 39857592
- PMCID: PMC11763200
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13010008
SSL5-AnxA5 Fusion Protein Constructed Based on Human Atherosclerotic Plaque scRNA-Seq Data Preventing the Binding of Apoptotic Endothelial Cells, Platelets, and Inflammatory Cells
Abstract
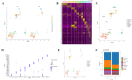
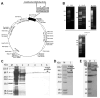
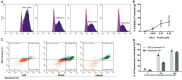
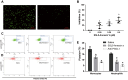
Background and aims: Coronary obstruction following plaque rupture is a critical pathophysiological change in the progression of stable angina (SAP) to acute coronary syndrome (ACS). The accumulation of platelets and various inflammatory cells on apoptotic endothelial cells is a key factor in arterial obstruction after plaque rupture. Through single-cell sequencing analysis (scRNA-seq) of plaques from SAP and ACS patients, we identified significant changes in the annexin V and P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 pathways. Staphylococcal superantigen-like 5 (SSL5) is an optimal antagonist P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 (PSGL1), while annexin V (AnxA5) can precisely detect dead cells in vivo. We constructed the SSL5-AnxA5 fusion protein and observed its role in preventing the interaction between apoptotic endothelial cells, platelets, and inflammatory cells. Methods: The scRNA-seq data were extracted from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. Single-cell transcriptome analysis results and cell-cell communication were analyzed to identify the ACS and SAP cell clusters and elucidate the intercellular communication differences. Then, we constructed and verified a fusion protein comprising SSL5 and AnxA5 domains via polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and Western blot. The binding capacity of the fusion protein to P-selectin and apoptotic cells was evaluated by flow cytometry and AnxA5-FITC apoptosis detection kit, respectively. Furthermore, co-incubation and immunofluorescence allowed us to describe the mediation effect of it between inflammatory cells and endothelial cells or activated platelets. Results: Our analysis of the scRNA-seq data showed that SELPLG (PSGL1 gene) and ANNEXIN had higher information flowing in ACS compared to SAP. The SELPLG signaling pathway network demonstrated a higher number of interactions in ACS, while the ANNEXIN signaling pathway network revealed stronger signaling from macrophages toward monocytes in ACS compared to SAP. Competition binding experiments with P-selectin showed that SSL5-AnxA5 induced a decrease in the affinity of PSGL1. SSL5-AnxA5 effectively inhibited the combination of endothelial cells with inflammatory cells and the interaction of activated platelets with inflammatory cells. Additionally, this fusion protein exhibited remarkable capability in binding to apoptotic cells. Conclusions: The bifunctional protein SSL5-AnxA5 exhibits promising potential as a protective agent against local inflammation in arterial tissues, making it an excellent candidate for PSGL1-related therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: P-selectin; acute coronary syndrome; fusion protein; stable angina; superantigen-like 5.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Staphylococcal SSL5 binding to human leukemia cells inhibits cell adhesion to endothelial cells and platelets.Cell Oncol. 2010;32(1-2):1-10. doi: 10.3233/CLO-2009-0486. Cell Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20208131 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcal superantigen-like 5 binds PSGL-1 and inhibits P-selectin-mediated neutrophil rolling.Blood. 2007 Apr 1;109(7):2936-43. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-06-015461. Blood. 2007. PMID: 17132726
-
Staphylococcal superantigen-like 5 activates platelets and supports platelet adhesion under flow conditions, which involves glycoprotein Ibalpha and alpha IIb beta 3.J Thromb Haemost. 2009 Nov;7(11):1867-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03564.x. Epub 2009 Jul 28. J Thromb Haemost. 2009. PMID: 19656281
-
Staphylococcal SSL5-induced platelet microparticles provoke proinflammatory responses via the CD40/TRAF6/NFκB signalling pathway in monocytes.Thromb Haemost. 2016 Mar;115(3):632-45. doi: 10.1160/TH15-04-0322. Epub 2015 Dec 3. Thromb Haemost. 2016. PMID: 26632487
-
ANXA5: related mechanisms of osteogenesis and additional biological functions.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Apr 24;13:1553683. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1553683. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40342928 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- W.H.O. Cardiovascular Diseases. [(accessed on 20 October 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/news-room/fact-sheets/item/cardiovascular-dis....
-
- Conrad N., Molenberghs G., Verbeke G., Zaccardi F., Lawson C., Friday J.M., Su H., Jhund P.S., Sattar N., Rahimi K., et al. Trends in cardiovascular disease incidence among 22 million people in the UK over 20 years: Population based study. Br. Med. J. 2024;387:e078523. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2023-078523. Correction in Br. Med. J. 2024, 387, q2381. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- He L., Chen Q., Wang L., Pu Y., Huang J., Cheng C.K., Luo J.Y., Kang L., Lin X., Xiang L., et al. Activation of Nrf2 inhibits atherosclerosis in ApoE(-/-) mice through suppressing endothelial cell inflammation and lipid peroxidation. Redox Biol. 2024;74:103–229. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103229. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

