An Analysis of the Effectiveness and Safety of Upadacitinib in the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Multicenter Real-World Study
- PMID: 39857773
- PMCID: PMC11761900
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13010190
An Analysis of the Effectiveness and Safety of Upadacitinib in the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Multicenter Real-World Study
Abstract
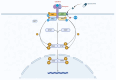
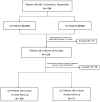
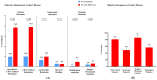
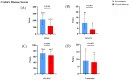
Background and Aims: Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) requires effective treatment options. Upadacitinib, a Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) inhibitor, has shown effectiveness in trials for Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC). This study evaluates its real-world effectiveness and safety. Methods: We conducted a multicenter retrospective cohort study in tertiary care centers, involving patients treated with upadacitinib from January 2023 to September 2024. The study included adult patients aged 18 years or older, diagnosed with UC or CD, who received at least 8 weeks of upadacitinib therapy. Treatment outcomes were evaluated using established clinical, endoscopic, imaging, histological, and laboratory parameters. Results: A total of 236 IBD patients received upadacitinib treatment. In 80 UC patients at 8 weeks, 64.0% achieved steroid-free remission, 57.6% clinical remission, and 81.8% response. Endoscopic remission was 35.8% (p = 0.039), with 63.3% response and 35.8% mucosal healing. Histological remission reached 29.2% (p = 0.009). For 156 CD patients at 12 weeks, 76.8% achieved steroid-free remission (p < 0.001), 77.8% clinical remission (p < 0.001), and 81.0% response. Mean CDAI decreased from 214.9 to 117.5 (p < 0.001). Endoscopic remission was 19.4%, with 48.9% response and 4.9% mucosal healing. Radiological remission was 9.1% with 85.7% response. Intestinal ultrasound showed 5.7% remission and 56.7% response. Conclusions: Upadacitinib demonstrates significant real-world effectiveness and safety in IBD, particularly in biologic-resistant cases, as evidenced by high rates of steroid-free remission and clinical response. These outcomes are likely due to its targeted JAK1 inhibition, which effectively reduces inflammation and promotes mucosal healing. Future research should focus on long-term safety, comparative effectiveness with other biologics, and its application in diverse patient populations. These findings support the integration of upadacitinib into IBD management strategies.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; inflammatory bowel disease; ulcerative colitis; upadacitinib.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
- 81900490 81670477 and 82270544/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2014008/Project 5010 of Sun Yat-Sen University
- 1010PY(2020)-55/Project 1010 of Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University
- 2024A03J0791/Guangzhou Science and Technology Fund
- CCCF-QF-2022A53-2 and CCCF-QF-2022B43-14/Qingfeng Scientific Research Fund of the China Crohn's & Colitis Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

