The Impact of a Music- and Movement-Based Intervention on Motor Competence, Social Engagement, and Behavior in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder
- PMID: 39857918
- PMCID: PMC11764137
- DOI: 10.3390/children12010087
The Impact of a Music- and Movement-Based Intervention on Motor Competence, Social Engagement, and Behavior in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder
Abstract
Background/objectives: The main objective of this manuscript is to evaluate the effects of training, music, and movement intervention on motor functions, social engagement, and behaviors in autistic children.
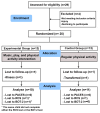
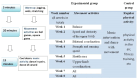
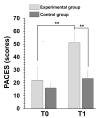
Methods: Twenty-one children with a diagnosis of mild autism spectrum disorder (ASD), with an age range of 5-to-13 years, were divided into two groups: the experimental group (n = 10) and the control group (n = 11). All participants were examined before (T0) and after the intervention (T1) to evaluate their motor functions (Bruininks-Oseretsky Motor Performance Test (BOT-2)), maladaptive behavior (RCS (Response to Challenge Scale)), and enjoyment and engagement (PACES (Physical Activity Enjoyment Scale)).
Results: Statistical analysis showed that music and movement intervention significantly improved motor functions such as balance and bilateral coordination (p < 0.0001), social engagement (p = 0.002), and adaptive behaviors (p = 0.005) in children with ASD. Our research supports the feasibility of music and movement intervention and documents the interest in participating in children with ASD.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates the benefits of movement and music interventions and can be considered a useful way to manage autism spectrum disorders in the future.
Keywords: autism spectrum disorder (ASD); intervention; motor functions; movement; music; physical activity; social engagement; stereotypical behavior.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beyond Broadway: Analysis of Qualitative Characteristics of and Individual Responses to Creatively Able, a Music and Movement Intervention for Children with Autism.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Apr 17;16(8):1377. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16081377. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 30999560 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing motor performance, praxis, coordination, and interpersonal synchrony between children with and without Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD).Res Dev Disabil. 2018 Jan;72:79-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2017.10.025. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Res Dev Disabil. 2018. PMID: 29121516 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Motor Interventions on Functional Performance Among Preschool Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial.Am J Occup Ther. 2023 Nov 1;77(6):7706205020. doi: 10.5014/ajot.2023.050283. Am J Occup Ther. 2023. PMID: 37992052 Clinical Trial.
-
The potential role of rhythmic entrainment and music therapy intervention for individuals with autism spectrum disorders.J Exerc Rehabil. 2019 Apr 26;15(2):180-186. doi: 10.12965/jer.1836578.289. eCollection 2019 Apr. J Exerc Rehabil. 2019. PMID: 31110998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Music Therapy for Children With Autistic Spectrum Disorder and/or Other Neurodevelopmental Disorders: A Systematic Review.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Apr 9;12:643234. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.643234. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33897497 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

