The Whole-Body MRI Reporting and Data System Guidelines for Prostate Cancer (MET-RADS-P), Multiple Myeloma (MY-RADS), and Cancer Screening (ONCO-RADS)
- PMID: 39858056
- PMCID: PMC11763526
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17020275
The Whole-Body MRI Reporting and Data System Guidelines for Prostate Cancer (MET-RADS-P), Multiple Myeloma (MY-RADS), and Cancer Screening (ONCO-RADS)
Abstract
Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging (WB-MRI) is being employed with increasing frequency to evaluate a broader spectrum of patients with diverse types of cancer and for cancer screening purposes. While clinical guidelines support its use, a standardized radiological approach is still lacking. To improve consistency in the acquisition, interpretation, and reporting of WB-MRI examinations, three reporting and data systems (RADSs) have been recently suggested: METastasis Reporting and Data System for Prostate Cancer (MET-RADS-P), Myeloma Response Assessment and Diagnosis System (MY-RADS), and Oncologically Relevant Findings Reporting and Data System (ONCO-RADS). MET-RADS-P was developed to stage and monitor men with advanced prostate cancer using WB-MRI. It has emerged as a reliable imaging biomarker for predicting metastatic disease progression and assessing treatment response. MY-RADS was developed to stage and monitor patients with multiple myeloma using WB-MRI, emerging as a prognostic imaging biomarker. However, the evidence regarding inter-reader agreement for MY-RADS is currently limited. ONCO-RADS was developed to standardize the use of WB-MRI for cancer screening in individuals with cancer predisposition syndromes and in the general population. While initial findings are promising, the evidence supporting its use remains limited. To further validate and expand upon these promising preliminary findings, additional large-scale, prospective, multicenter studies are necessary.
Keywords: MET-RADS-P; MRI scans; MY-RADS; ONCO-RADS; RADS; clinical oncology; narrative review; practice guidelines; radiology; whole-body magnetic resonance imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
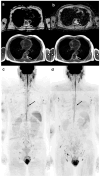
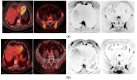
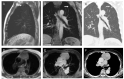
Similar articles
-
Applying ONCO-RADS to whole-body MRI cancer screening in a retrospective cohort of asymptomatic individuals.Cancer Imaging. 2024 Feb 7;24(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s40644-024-00665-z. Cancer Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38326850 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging (WB-MRI) reporting with the METastasis Reporting and Data System for Prostate Cancer (MET-RADS-P): inter-observer agreement between readers of different expertise levels.Cancer Imaging. 2020 Oct 27;20(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s40644-020-00350-x. Cancer Imaging. 2020. PMID: 33109268 Free PMC article.
-
Oncologically Relevant Findings Reporting and Data System (ONCO-RADS): Guidelines for the Acquisition, Interpretation, and Reporting of Whole-Body MRI for Cancer Screening.Radiology. 2021 Jun;299(3):494-507. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2021201740. Epub 2021 Apr 27. Radiology. 2021. PMID: 33904776 Review.
-
METastasis Reporting and Data System for Prostate Cancer: Practical Guidelines for Acquisition, Interpretation, and Reporting of Whole-body Magnetic Resonance Imaging-based Evaluations of Multiorgan Involvement in Advanced Prostate Cancer.Eur Urol. 2017 Jan;71(1):81-92. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.05.033. Epub 2016 Jun 14. Eur Urol. 2017. PMID: 27317091 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-body MRI in oncology: acquisition protocols, current guidelines, and beyond.Radiol Med. 2024 Sep;129(9):1352-1368. doi: 10.1007/s11547-024-01851-6. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Radiol Med. 2024. PMID: 38990426 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Neck Imaging Reporting and Data System (NI-RADS) in the Management of Head and Neck Cancers.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Apr 8;12(4):398. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12040398. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40281758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of whole-body diffusion-weighted imaging with background body signal suppression in CRPC patients undergoing Ra-223 therapy: an exploratory analysis.Jpn J Radiol. 2025 Jun 17. doi: 10.1007/s11604-025-01817-2. Online ahead of print. Jpn J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40526365
References
-
- Eustace S., Tello R., DeCarvalho V., Carey J., Wroblicka J.T., Melhem E.R., Yucel E.K. A Comparison of Whole-Body turboSTIR MR Imaging and Planar 99mTc-Methylene Diphosphonate Scintigraphy in the Examination of Patients with Suspected Skeletal Metastases. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1997;169:1655–1661. doi: 10.2214/ajr.169.6.9393186. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Walker R., Kessar P., Blanchard R., Dimasi M., Harper K., DeCarvalho V., Yucel E.K., Patriquin L., Eustace S. Turbo STIR Magnetic Resonance Imaging as a Whole-Body Screening Tool for Metastases in Patients with Breast Carcinoma: Preliminary Clinical Experience. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 2000;11:343–350. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1522-2586(200004)11:4<343::AID-JMRI1>3.0.CO;2-P. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

