Anxiolytic, Antidepressant, and Anticholinesterase Effects of Essential Oil from Myrcia sylvatica (G.Mey.) DC
- PMID: 39858504
- PMCID: PMC11764472
- DOI: 10.3390/biom15010110
Anxiolytic, Antidepressant, and Anticholinesterase Effects of Essential Oil from Myrcia sylvatica (G.Mey.) DC
Abstract
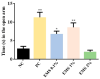
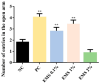
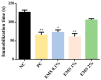
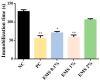
Aromatic plants are rich sources of essential oils (EOs), recognized for their therapeutic properties due to their diversity of phytochemicals. This study investigated the anxiolytic and antidepressant effects of Myrcia sylvatica essential oil (MsEO) through inhalation in an animal model and its in vitro anticholinesterase (AChE) activity. The EO was obtained by hydrodistillation, and its volatile constituents were analyzed by GC-MS. Swiss mice were exposed to doses of 0.1%, 1%, and 2% of the EO via an inhalation apparatus. The anxiolytic activity was assessed using the elevated plus maze and light-dark box tests, while antidepressant activity was evaluated using the tail suspension and forced swimming tests. To examine potential side effects, the animals were subjected to rotarod, Y-maze, and Morris water maze tests to assess motor coordination, memory, and learning. Anticholinesterase activity was determined by direct bioautography and colorimetry based on the Ellman method. The results demonstrated that inhalation of MsEO at doses of 0.1% and 1% significantly reduced anxiety and depressive-like behaviors without impairing memory, learning, or motor coordination in the animals. Moreover, MsEO inhibited acetylcholinesterase with an IC50 of 0.47 μg/mL. These findings suggest that MsEO has potential therapeutic applications for anxiety and depression disorders, with additional anticholinesterase activity warranting further investigation in cognitive-related conditions.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; anxiety; aromatherapy; central nervous system; depression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Inhaled Litsea glaucescens K. (Lauraceae) leaves' essential oil has anxiolytic and antidepressant-like activity in mice by BDNF pathway activation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Mar 1;321:117489. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117489. Epub 2023 Nov 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38012973
-
SuHeXiang Essential Oil Inhalation Produces Antidepressant- and Anxiolytic-Like Effects in Adult Mice.Biol Pharm Bull. 2018 Jul 1;41(7):1040-1048. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b18-00082. Epub 2018 May 9. Biol Pharm Bull. 2018. PMID: 29743387
-
The Effects of Inhaled Pimpinella peregrina Essential Oil on Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment, Anxiety, and Depression in Laboratory Rats.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Nov;53(9):6557-6567. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9693-9. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26768430
-
Anthriscus nemorosa essential oil inhalation prevents memory impairment, anxiety and depression in scopolamine-treated rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Dec;84:1313-1320. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.10.075. Epub 2016 Oct 29. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27810788
-
Anxiolytic Terpenoids and Aromatherapy for Anxiety and Depression.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1260:283-296. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-42667-5_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32304038 Review.
Cited by
-
Essential Oil of Lippia origanoides Kunth: Nanoformulation, Anticholinesterase Activity, and Molecular Docking.Molecules. 2025 Mar 31;30(7):1554. doi: 10.3390/molecules30071554. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40286153 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Mental Health: Strengthening Our Response. [(accessed on 14 August 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mental-health-strengthe....
-
- Cipriani A., Furukawa T.A., Salanti G., Geddes J.R., Higgins J.P., Churchill R., Watanabe N., Nakagawa A., Omori I.M., McGuire H., et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 new-generation antidepressants: A multiple-treatments meta-analysis. Lancet. 2009;373:746–758. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60046-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Benari O.M., Springer R.R., Almog G.B., Yore I.B., Zadok M.B., Lin H.-M.S., Ouyang Y.M., Sano M., Bendlin B.B., Livny A., et al. Behavioral and Brain Correlates of Emotional Distress in Older Adults During COVID-19 Quarantine. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2023;37:156–159. doi: 10.1097/WAD.0000000000000540. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

