Recent Advances in Antimicrobial Resistance: Insights from Escherichia coli as a Model Organism
- PMID: 39858819
- PMCID: PMC11767524
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13010051
Recent Advances in Antimicrobial Resistance: Insights from Escherichia coli as a Model Organism
Abstract
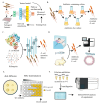
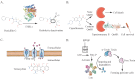
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) represents a critical global health threat, and a thorough understanding of resistance mechanisms in Escherichia coli is needed to guide effective treatment interventions. This review explores recent advances for investigating AMR in E. coli, including machine learning for resistance pattern analysis, laboratory evolution to generate resistant mutants, mutant library construction, and genome sequencing for in-depth characterization. Key resistance mechanisms are discussed, including drug inactivation, target modification, altered transport, and metabolic adaptation. Additionally, we highlight strategies to mitigate the spread of AMR, such as dynamic resistance monitoring, innovative therapies like phage therapy and CRISPR-Cas technology, and tighter regulation of antibiotic use in animal production systems. This review provides actionable insights into E. coli resistance mechanisms and identifies promising directions for future antibiotic development and AMR management.
Keywords: AMR prevention; Escherichia coli; antimicrobial resistance; machine learning; synthetic biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Xiao R., Li Y., Liu X., Ding Y., Lai J., Li Y., Kang W., Zou P., Wang J., Du Y., et al. Antibiotic susceptibility of Escherichia coli isolated from neonates admitted to neonatal intensive care units across China from 2015 to 2020. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023;13:1183736. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1183736. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

