GmGIF5 Promotes Cell Expansion by Negatively Regulating Cell Wall Modification
- PMID: 39859208
- PMCID: PMC11765367
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26020492
GmGIF5 Promotes Cell Expansion by Negatively Regulating Cell Wall Modification
Abstract
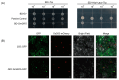
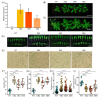
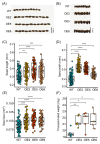
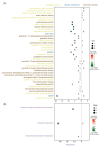
Soybean is an important and versatile crop worldwide. Enhancing soybean architecture offers a potential method to increase yield. Plant-specific transcription factors play a crucial, yet often unnoticed, role in regulating plant growth and development. GRF-INTERACTING FACTOR (GIF) genes are plant-specific transcription factors; however, their functions in soybean remain poorly understood. Eight GmGIF members were identified in soybean (Glycine max L.). Phylogenetic analysis divided the eight GmGIF proteins into three groups. In this study, we focused on the role of GmGIF5 owing to its high expression level in the meristem. Subcellular localization and transcriptional activity analysis showed that GmGIF5 was localized to the nucleus and has self-transactivation ability. To elucidate the biological function of GmGIF5, we constructed transgenic Arabidopsis lines overexpressing the gene. Phenotype observations indicated that the overexpression of GmGIF5 contributed to larger leaves, higher plants, wider stems, and larger seeds. The organs of GmGIF5 overexpression lines exhibited larger sizes primarily due to an increase in cell size rather than cell number. RNA sequencing was performed to investigate the underlying mechanism for these effects, showing that differentially expressed genes in overexpression lines were mainly enriched in cell wall modification processes. Our study provides new clues for an understanding of the roles of the GmGIF family in soybean, which can promote the further application of these genes in genetic breeding.
Keywords: GRF-INTERACTING FACTORs; RNA-seq; cell expansion; soybean; transcription factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Machado F.B., Moharana K.C., Almeida-Silva F., Gazara R.K., Pedrosa-Silva F., Coelho F.S., Grativol C., Venancio T.M. Systematic Analysis of 1298 RNA-seq Samples and Construction of a Comprehensive Soybean (Glycine max) Expression Atlas. Plant J. 2020;103:1894–1909. doi: 10.1111/tpj.14850. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen L., Yang H., Fang Y., Guo W., Chen H., Zhang X., Dai W., Chen S., Hao Q., Yuan S., et al. Overexpression of GmMYB14 Improves High-Density Yield and Drought Tolerance of Soybean through Regulating Plant Architecture Mediated by the Brassinosteroid Pathway. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021;19:702–716. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13496. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang H.W., Zhang B., Hao Y.J., Huang J., Tian A.G., Liao Y., Zhang J.S., Chen S.Y. The Soybean Dof-Type Transcription Factor Genes, GmDof4 and GmDof11, Enhance Lipid Content in the Seeds of Transgenic Arabidopsis Plants. Plant J. 2007;52:716–729. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03268.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

