Ultrastructural Study and Immunohistochemical Characteristics of Mesencephalic Tegmentum in Juvenile Chum Salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) Brain After Acute Traumatic Injury
- PMID: 39859360
- PMCID: PMC11765592
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26020644
Ultrastructural Study and Immunohistochemical Characteristics of Mesencephalic Tegmentum in Juvenile Chum Salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) Brain After Acute Traumatic Injury
Abstract
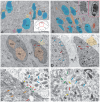
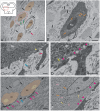
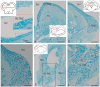
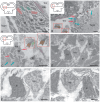
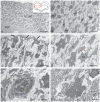
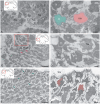
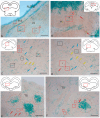
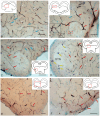
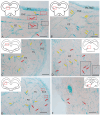
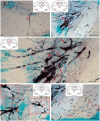
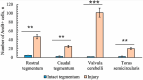
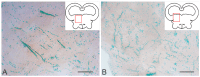
The ultrastructural organization of the nuclei of the tegmental region in juvenile chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) was examined using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The dorsal tegmental nuclei (DTN), the nucleus of fasciculus longitudinalis medialis (NFLM), and the nucleus of the oculomotor nerve (NIII) were studied. The ultrastructural examination provided detailed ultrastructural characteristics of neurons forming the tegmental nuclei and showed neuro-glial relationships in them. Neurons of three size types with a high metabolic rate, characterized by the presence of numerous mitochondria, polyribosomes, Golgi apparatus, and cytoplasmic inclusions (vacuoles, lipid droplets, and dense bodies), were distinguished. It was found that large interneurons of the NFLM formed contacts with protoplasmic astrocytes. Excitatory synaptic structures were identified in the tegmentum and their detailed characteristic are provided for the first time. Microglia-like cells were found in the NIII. The ultrastructural characteristics of neurogenic zones of the tegmentum of juvenile chum salmon were also determined for the first time. In the neurogenic zones of the tegmentum, adult-type neural stem progenitor cells (aNSPCs) corresponding to cells of types III and IVa Danio rerio. In the neurogenic zones of the tegmentum, neuroepithelial-like cells (NECs) corresponding to cells previously described from the zebrafish cerebellum were found and characterized. In the tegmentum of juvenile chum salmon, patterns of paracrine neurosecretion were observed and their ultrastructural characteristics were recorded. Patterns of apoptosis in large neurons of the tegmentum were examined by TEM. Using immunohistochemical (IHC) labeling of the brain lipid-binding protein (BLBP) and aromatase B (AroB), patterns of their expression in the tegmentum of intact animals and in the post-traumatic period after acute injury to the medulla oblongata were characterized. The response to brainstem injury in chum salmon was found to activate multiple signaling pathways, which significantly increases the BLBP and AroB expression in various regions of the tegmentum and valvula cerebelli. However, post-traumatic patterns of BLBP and AroB localizations are not the same. In addition to a general increase in BLBP expression in the tegmental parenchyma, BLBP overexpression was observed in the rostro-lateral tegmental neurogenic zone (RLTNZ), while AroB expression in the RLTNZ was completely absent. Another difference was the peripheral overexpression of AroB and the formation of dense reactive clusters in the ventro-medial zone of the tegmentum. Thus, in the post-traumatic period, various pathways were activated whose components were putative candidates for inducers of the "astrocyte-like" response in the juvenile chum salmon brain that are similar to those present in the mammalian brain. In this case, BLBP acted as a factor enhancing the differentiation of both radial glia and neurons. Estradiol from AroB+ astrocytes exerted paracrine neuroprotective effects through the potential inhibition of inflammatory processes. These results indicate a new role for neuronal aromatization as a mechanism preventing the development of neuroinflammation. Moreover, our findings support the hypothesis that BLBP is a factor enhancing neuronal and glial differentiation in the post-traumatic period in the chum salmon brain.
Keywords: Oncorhynchus keta; aromatase B; brain lipid-binding protein; dorsal tegmental nucleus; nucleus of fasciculus longitudinalis medialis; nucleus of oculomotor nerve; tegmentum; transmission electron microscope.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
A Confocal Microscopic Study of Gene Transfer into the Mesencephalic Tegmentum of Juvenile Chum Salmon, Oncorhynchus keta, Using Mouse Adeno-Associated Viral Vectors.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 26;22(11):5661. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115661. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34073457 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical Brain Injury Increases Cells' Production of Cystathionine β-Synthase and Glutamine Synthetase, but Reduces Pax2 Expression in the Telencephalon of Juvenile Chum Salmon, Oncorhynchus keta.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 28;22(3):1279. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031279. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33525421 Free PMC article.
-
Neural Stem Cells/Neuronal Precursor Cells and Postmitotic Neuroblasts in Constitutive Neurogenesis and After ,Traumatic Injury to the Mesencephalic Tegmentum of Juvenile Chum Salmon, Oncorhynchus keta.Brain Sci. 2020 Jan 25;10(2):65. doi: 10.3390/brainsci10020065. Brain Sci. 2020. PMID: 31991815 Free PMC article.
-
Post-Traumatic Expressions of Aromatase B, Glutamine Synthetase, and Cystathionine-Beta-Synthase in the Cerebellum of Juvenile Chum Salmon, Oncorhynchus keta.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 14;25(6):3299. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063299. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542274 Free PMC article.
-
Transduction of Brain Neurons in Juvenile Chum Salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) with Recombinant Adeno-Associated Hippocampal Virus Injected into the Cerebellum during Long-Term Monitoring.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 29;23(9):4947. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094947. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563338 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Babchenko V.Y., Belova A.S., Bashirzade A.A., Peskov A.V., Giniatullina A.N., Shchegolev B.F. Models of Traumatic Brain Injury in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Ross. Fiziol. Zhurnal Im. IM Sechenova. 2021;107:1059–1076. doi: 10.1007/s11055-022-01254-y. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

