Exosomal Liquid Biopsy in Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review of Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment Response
- PMID: 39859516
- PMCID: PMC11765602
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26020802
Exosomal Liquid Biopsy in Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review of Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment Response
Abstract
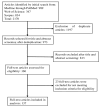
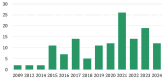
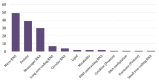
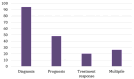
Prostate cancer, a leading cause of cancer-related mortality among men, often presents challenges in accurate diagnosis and effective monitoring. This systematic review explores the potential of exosomal biomolecules as noninvasive biomarkers for the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment response of prostate cancer. A thorough systematic literature search through online public databases (Medline via PubMed, Scopus, and Web of science) using structured search terms and screening using predefined eligibility criteria resulted in 137 studies that we analyzed in this systematic review. We evaluated the findings from these clinical studies, revealing that the load of exosomes in the blood and urine of prostate cancer patients, which includes microRNAs (miRNAs), proteins, and lipids, demonstrates disease-specific changes. It also shows that some exosomal markers can differentiate between malignant and benign hyperplasia of the prostate, predict disease aggressiveness, and monitor treatment efficacy. Notably, miRNA emerged as the most frequently studied biomolecule, demonstrating superior diagnostic potential compared to traditional methods like prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing. The analysis also highlights the pressing need for a standardised analytic approach through multi-centre studies to validate the full potential of exosomal biomarkers for the diagnosis and monitoring of prostate cancer.
Keywords: biomarkers; exosomes; liquid biopsy; miRNA; prognosis; prostate cancer; response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ioannidou E., Moschetta M., Shah S., Parker J.S., Ozturk M.A., Pappas-Gogos G., Sheriff M., Rassy E., Boussios S. Angiogenesis and Anti-Angiogenic Treatment in Prostate Cancer: Mechanisms of Action and Molecular Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:9926. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189926. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Merriel S.W.D., Pocock L., Gilbert E., Creavin S., Walter F.M., Spencer A., Hamilton W. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) for the detection of prostate cancer in symptomatic patients. BMC Med. 2022;20:54. doi: 10.1186/s12916-021-02230-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

