A Study on Potential Sources of Perineuronal Net-Associated Sema3A in Cerebellar Nuclei Reveals Toxicity of Non-Invasive AAV-Mediated Cre Expression in the Central Nervous System
- PMID: 39859534
- PMCID: PMC11765860
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26020819
A Study on Potential Sources of Perineuronal Net-Associated Sema3A in Cerebellar Nuclei Reveals Toxicity of Non-Invasive AAV-Mediated Cre Expression in the Central Nervous System
Abstract
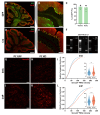
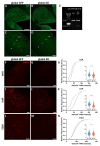
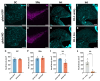
Semaphorin 3A (Sema3A) is an axon guidance molecule, which is also abundant in the adult central nervous system (CNS), particularly in perineuronal nets (PNNs). PNNs are extracellular matrix structures that restrict plasticity. The cellular sources of Sema3A in PNNs are unknown. Most Sema3A-bearing neurons do not express Sema3A mRNA, suggesting that Sema3A may be released from other neurons. Another potential source of Sema3A is the choroid plexus. To identify sources of PNN-associated Sema3A, we focused on the cerebellar nuclei, which contain Sema3A+ PNNs. Cerebellar nuclei neurons receive prominent input from Purkinje cells (PCs), which express high levels of Sema3A mRNA. By using a non-invasive viral vector approach, we overexpressed Cre in PCs, the choroid plexus, or throughout the CNS of Sema3Afl/fl mice. Knocking out Sema3A in PCs or the choroid plexus was not sufficient to decrease the amount of PNN-associated Sema3A. Alternatively, knocking out Sema3A throughout the CNS induced a decrease in PNN-associated Sema3A. However, motor deficits, microgliosis, and neurodegeneration were observed, which were due to Cre toxicity. Our study represents the first attempt to unravel cellular sources of PNN-associated Sema3A and shows that non-invasive viral-mediated Cre expression throughout the CNS could lead to toxicity, complicating the interpretation of Cre-mediated Sema3A knock-out.
Keywords: AAV-PHP.eB; Cre; Purkinje cells; Semaphorin 3A; cerebellar nuclei; choroid plexus; perineuronal nets; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Modulation of semaphorin3A in perineuronal nets during structural plasticity in the adult cerebellum.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013 Nov;57:10-22. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2013.08.003. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23999154
-
The chemorepulsive axon guidance protein semaphorin3A is a constituent of perineuronal nets in the adult rodent brain.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013 Sep;56:186-200. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2013.04.009. Epub 2013 May 9. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23665579
-
Perineuronal Nets in the Deep Cerebellar Nuclei Regulate GABAergic Transmission and Delay Eyeblink Conditioning.J Neurosci. 2018 Jul 4;38(27):6130-6144. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3238-17.2018. Epub 2018 Jun 1. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29858484 Free PMC article.
-
The Chemorepulsive Protein Semaphorin 3A and Perineuronal Net-Mediated Plasticity.Neural Plast. 2016;2016:3679545. doi: 10.1155/2016/3679545. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Neural Plast. 2016. PMID: 27057361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulatory Effects of Monoamines and Perineuronal Nets on Output of Cerebellar Purkinje Cells.Front Neural Circuits. 2021 Jun 14;15:661899. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2021.661899. eCollection 2021. Front Neural Circuits. 2021. PMID: 34194302 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Giger R.J., Pasterkamp R.J., Heijnen S., Holtmaat A.J.G.D., Verhaagen J. Anatomical Distribution of the Chemorepellent Semaphorin III/Collapsin-1 in the Adult Rat and Human Brain: Predominant Expression in Structures of the Olfactory-Hippocampal Pathway and the Motor System. J. Neurosci. Res. 1998;52:27–42. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19980401)52:1<27::AID-JNR4>3.0.CO;2-M. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vo T., Carulli D., Ehlert E.M.E., Kwok J.C.F., Dick G., Mecollari V., Moloney E.B., Neufeld G., De Winter F., Fawcett J.W., et al. The Chemorepulsive Axon Guidance Protein semaphorin3A Is a Constituent of Perineuronal Nets in the Adult Rodent Brain. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2013;56:186–200. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2013.04.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dick G., Tan C.L., Alves J.N., Ehlert E.M.E., Miller G.M., Hsieh-Wilson L.C., Sugahara K., Oosterhof A., Van Kuppevelt T.H., Verhaagen J., et al. Semaphorin 3A Binds to the Perineuronal Nets via Chondroitin Sulfate Type E Motifs in Rodent Brains. J. Biol. Chem. 2013;288:27384–27395. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.310029. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

