Endoscopic-Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation for Pancreatic Tumors
- PMID: 39860500
- PMCID: PMC11765552
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14020495
Endoscopic-Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation for Pancreatic Tumors
Abstract
Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a promising minimally invasive technique for the treatment of pancreatic lesions. This review first focuses on the technical aspects in EUS-RFA: the procedure typically employs EUS probes with integrated radiofrequency electrodes, enabling accurate targeting and ablation of pancreatic lesions. Different types of RFA devices, monopolar and bipolar energy delivery systems, are discussed, along with considerations for optimal ablation, including energy settings, procedure time, and pre- and post-procedural management. This paper presents a comprehensive literature review of EUS-RFA applied to both solid and cystic pancreatic lesions, including functioning and non-functioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNETs), pancreatic cystic lesions (PCLs), pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), and pancreatic metastases (PMs), discussing current evidence on safety, efficacy, clinical outcomes, and adverse events (AEs). EUS-RFA is an emerging technique with expanding potential for the treatment of both benign and malignant conditions; however, further studies are needed to better define patient selection criteria, assess long-term benefits, and establish definitive indications for its use.
Keywords: ablation; endoscopic ultrasound; locoregional therapy; pancreas; radiofrequency.
Conflict of interest statement
The following authors disclose financial relationships: C.C.: Speaker for Steris. C.B.: Speaker for Steris, Fujifilm, Boston Scientific, and Q3 Medical. C.F.: Consultant for Boston Scientific; speaker for Steris and Q3 Medical.
Figures
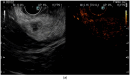

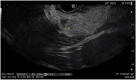
References
-
- Schuh F., Mihaljevic A.L., Probst P., Trudeau M.T., Müller P.C., Marchegiani G., Besselink M.G., Uzunoglu F., Izbicki J.R., Falconi M., et al. A Simple Classification of Pancreatic Duct Size and Texture Predicts Postoperative Pancreatic Fistula: A Classification of the International Study Group of Pancreatic Surgery. Ann. Surg. 2023;277:e597–e608. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000004855. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bassi C., Marchegiani G., Dervenis C., Sarr M., Abu Hilal M., Adham M., Allen P., Andersson R., Asbun H.J., Besselink M.G., et al. The 2016 Update of the International Study Group (ISGPS) Definition and Grading of Postoperative Pancreatic Fistula: 11 Years After. Surgery. 2017;161:584–591. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2016.11.014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Faraoni E.Y., O’Brien B.J., Strickland L.N., Osborn B.K., Mota V., Chaney J., Atkins C.L., Cen P., Rowe J., Cardenas J., et al. Radiofrequency Ablation Remodels the Tumor Microenvironment and Promotes Neutrophil-Mediated Abscopal Immunomodulation in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2023;11:4–12. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-22-0379. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

