EEG-to-EEG: Scalp-to-Intracranial EEG Translation Using a Combination of Variational Autoencoder and Generative Adversarial Networks
- PMID: 39860864
- PMCID: PMC11769358
- DOI: 10.3390/s25020494
EEG-to-EEG: Scalp-to-Intracranial EEG Translation Using a Combination of Variational Autoencoder and Generative Adversarial Networks
Abstract
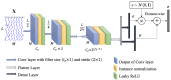
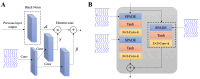
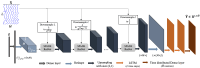
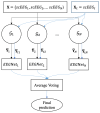
A generative adversarial network (GAN) makes it possible to map a data sample from one domain to another one. It has extensively been employed in image-to-image and text-to image translation. We propose an EEG-to-EEG translation model to map the scalp-mounted EEG (scEEG) sensor signals to intracranial EEG (iEEG) sensor signals recorded by foramen ovale sensors inserted into the brain. The model is based on a GAN structure in which a conditional GAN (cGAN) is combined with a variational autoencoder (VAE), named as VAE-cGAN. scEEG sensors are plagued by noise and suffer from low resolution. On the other hand, iEEG sensor recordings enjoy high resolution. Here, we consider the task of mapping the scEEG sensor information to iEEG sensors to enhance the scEEG resolution. In this study, our EEG data contain epileptic interictal epileptiform discharges (IEDs). The identification of IEDs is crucial in clinical practice. Here, the proposed VAE-cGAN is firstly employed to map the scEEG to iEEG. Then, the IEDs are detected from the resulting iEEG. Our model achieves a classification accuracy of 76%, an increase of, respectively, 11%, 8%, and 3% over the previously proposed least-square regression, asymmetric autoencoder, and asymmetric-symmetric autoencoder mapping models.
Keywords: IED detection; generative adversarial networks; interictal epileptiform discharge; scalp-to-intracranial EEG translation; variational autoencoder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Virtual Electroencephalogram Acquisition: A Review on Electroencephalogram Generative Methods.Sensors (Basel). 2025 May 18;25(10):3178. doi: 10.3390/s25103178. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40431969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of signal processing and machine learning techniques for interictal epileptiform discharge detection.Comput Biol Med. 2024 Jan;168:107782. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.107782. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Comput Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 38070202 Review.
-
Mapping Scalp to Intracranial EEG using Generative Adversarial Networks for Automatically Detecting Interictal Epileptiform Discharges.IEEE Stat Signal Processing Workshop. 2023 Jul 2;27:710-714. doi: 10.1109/SSP53291.2023.10207965. IEEE Stat Signal Processing Workshop. 2023. PMID: 39246603 Free PMC article.
-
Higher-order tensor decomposition based scalp-to-intracranial EEG projection for detection of interictal epileptiform discharges.J Neural Eng. 2021 Dec 24;18(6). doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ac3cc4. J Neural Eng. 2021. PMID: 34818640
-
Deep Neural Architectures for Mapping Scalp to Intracranial EEG.Int J Neural Syst. 2018 Oct;28(8):1850009. doi: 10.1142/S0129065718500090. Epub 2018 Mar 19. Int J Neural Syst. 2018. PMID: 29631503
Cited by
-
Virtual Electroencephalogram Acquisition: A Review on Electroencephalogram Generative Methods.Sensors (Basel). 2025 May 18;25(10):3178. doi: 10.3390/s25103178. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40431969 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sanei S., Chambers J.A. EEG Signal Processing and Machine Learning. John Wiley & Sons; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2021.
-
- Esfahani M.M., Najafi M.H., Sadati H. Optimizing EEG Signal Classification for Motor Imagery BCIs: FilterBank CSP with Riemannian Manifolds and Ensemble Learning Models; Proceedings of the 2023 9th International Conference on Signal Processing and Intelligent Systems (ICSPIS); Bali, Indonesia. 14–15 December 2023; Piscataway, NJ, USA: IEEE; 2023. pp. 1–6.
-
- Esfahani M.M., Sadati H. Application of NSGA-II in channel selection of motor imagery EEG signals with common spatio-spectral patterns in BCI systems; Proceedings of the 2022 8th International Conference on Control, Instrumentation and Automation (ICCIA); Tehran, Iran. 2–3 March 2022; Piscataway, NJ, USA: IEEE; 2022. pp. 1–6.
-
- Shirani S., Abdi-Sargezeh B., Valentin A., Alarcon G., Jarchi D., Bird J., Sanei S. Distributed Beamforming for Localization of Brain Seizure Sources from Intracranial EEG Array; Proceedings of the 2024 32nd European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO); Lyon, France. 26–30 August 2024; pp. 1117–1121. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

