Differentiation of Escherichia coli and Shigella flexneri by Metabolite Profiles Obtained Using Gold Nanoparticles-Based Surface-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry
- PMID: 39860979
- PMCID: PMC11768538
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens14010019
Differentiation of Escherichia coli and Shigella flexneri by Metabolite Profiles Obtained Using Gold Nanoparticles-Based Surface-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
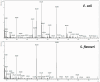
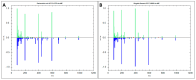
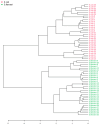
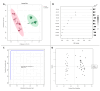
Escherichia coli and Shigella flexneri are challenging to differentiate using methods such as phenotyping, 16S rRNA sequencing, or protein profiling through matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI MS) due to their close relatedness. This study explores the potential for identifying E. coli and S. flexneri by incorporating reference spectra of metabolite profiles, obtained via surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (SALDI MS) employing gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), into the Bruker Biotyper database. Metabolite extracts from E. coli and S. flexneri cells were prepared using liquid-liquid extraction in a chloroform-methanol-water system. The extracts were analyzed using Au-SALDI MS in positive ion mode, and reference spectra, compiled from 30 spectra for each bacterium, were added to the database. Identification of bacteria based on metabolite fingerprints in the Biotyper database produced correct results with scores exceeding 2.75. The results of Partial Least Squares-Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA) demonstrated that the metabolomic approach could accurately differentiate the microorganisms under study. A panel of nine m/z values was also identified, each with an area under the ROC curve of above 0.8, enabling accurate identification of E. coli and S. flexneri. A search of metabolite databases allowed the following compounds to be assigned to the selected m/z values: N-acetylputrescine, arginine, 2-maleylacetate, benzoyl phosphate, N8-acetylspermidine, alanyl-glutamate, 4-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydrodipicolinate, and sucrose. The analyses showed that identification of bacteria based on metabolite profiles obtained by the Au-SALDI MS method is feasible and can be useful for distinguishing closely related microorganisms that are difficult to differentiate by other techniques.
Keywords: gold nanoparticles; identification; mass spectrometry; metabolites; microorganisms; surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lipidomic approach to identify Escherichia coli and Shigella spp. by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry.Adv Med Sci. 2024 Sep;69(2):238-247. doi: 10.1016/j.advms.2024.04.005. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Adv Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38670227
-
Discrimination of Escherichia coli, Shigella flexneri, and Shigella sonnei using lipid profiling by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry paired with machine learning.Microbiologyopen. 2022 Aug;11(4):e1313. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.1313. Microbiologyopen. 2022. PMID: 36004556 Free PMC article.
-
A novel short-term high-lactose culture approach combined with a matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry assay for differentiating Escherichia coli and Shigella species using artificial neural networks.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 8;14(10):e0222636. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222636. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31593573 Free PMC article.
-
Gold nanoparticles assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry and applications: from simple molecules to intact cells.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016 Jul;408(17):4485-502. doi: 10.1007/s00216-016-9374-6. Epub 2016 Mar 14. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016. PMID: 26973236 Review.
-
Nanoparticle-based laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometric analysis of drugs and metabolites.J Food Drug Anal. 2018 Oct;26(4):1215-1228. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2018.07.001. Epub 2018 Aug 14. J Food Drug Anal. 2018. PMID: 30249320 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brenner D.J., Fanning G.R., Miklos G.V., Steigerwalt A.G. Polynucleotide Sequence Relatedness Among Shigella Species. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1973;23:1–7. doi: 10.1099/00207713-23-1-1. - DOI
-
- Pazhani G.P., Niyogi S.K., Singh A.K., Sen B., Taneja N., Kundu M., Yamasaki S., Ramamurthy T. Molecular Characterization of Multidrug-Resistant Shigella Species Isolated from Epidemic and Endemic Cases of Shigellosis in India. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008;57:856–863. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.2008/000521-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Niyogi S.K. Shigellosis. J. Microbiol. 2005;43:133–143. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

